Is CryptoLocker still a threat?
Is CryptoLocker still a threat?
According to recent data from Google-owned threat intelligence firm Mandiant, the number of ransomware attacks dropped 15% between 2021 and 2022.
What happened to CryptoLocker?
CryptoLocker was isolated in late May 2014 via Operation Tovar, which took down the Gameover ZeuS botnet that had been used to distribute the malware.
How many people were infected by CryptoLocker?
Between September and December 2013, CryptoLocker infected more than 250,000 systems. It earned more than $3 million for its creators before the Gameover ZeuS botnet, which was used to carry out the attacks, was taken offline in 2014 in an international operation.
What is the target of the CryptoLocker Trojan attack?
It is a Trojan horse that infects your computer and then searches for files to encrypt. This includes anything on your hard drives and all connected media — for example, USB memory sticks or any shared network drives. In addition, the malware seeks out files and folders you store in the cloud.
Do I need to worry about ransomware?
Ransomware incidents can severely impact business processes and leave organizations without the data they need to operate and deliver mission-critical services.
Should I worry about ransomware?
Ransomware is a legitimate risk for anyone with a computer and data they want keep accessible and secure.
Can CryptoLocker be decrypted?
Once CryptoLocker encrypts your files, they’ll stay encrypted until you decrypt them with the correct key. Removing CryptoLocker prevents it from encrypting anything else, but it isn’t going to decrypt your files.
What is the largest ransomware payout?
Summary | Ransom Demanded
Colonial Pipeline paid $5 Million ransom one day after cyberattack, CEO tells Senate | $5 Million
JBS paid $11 Million to REvil ransomware, $22.5M first demanded | $22.5 Million
Insurance giant CNA fully restores systems after ransomware attack | $60 Million
REvil gang targets Kaseya | $70 Million
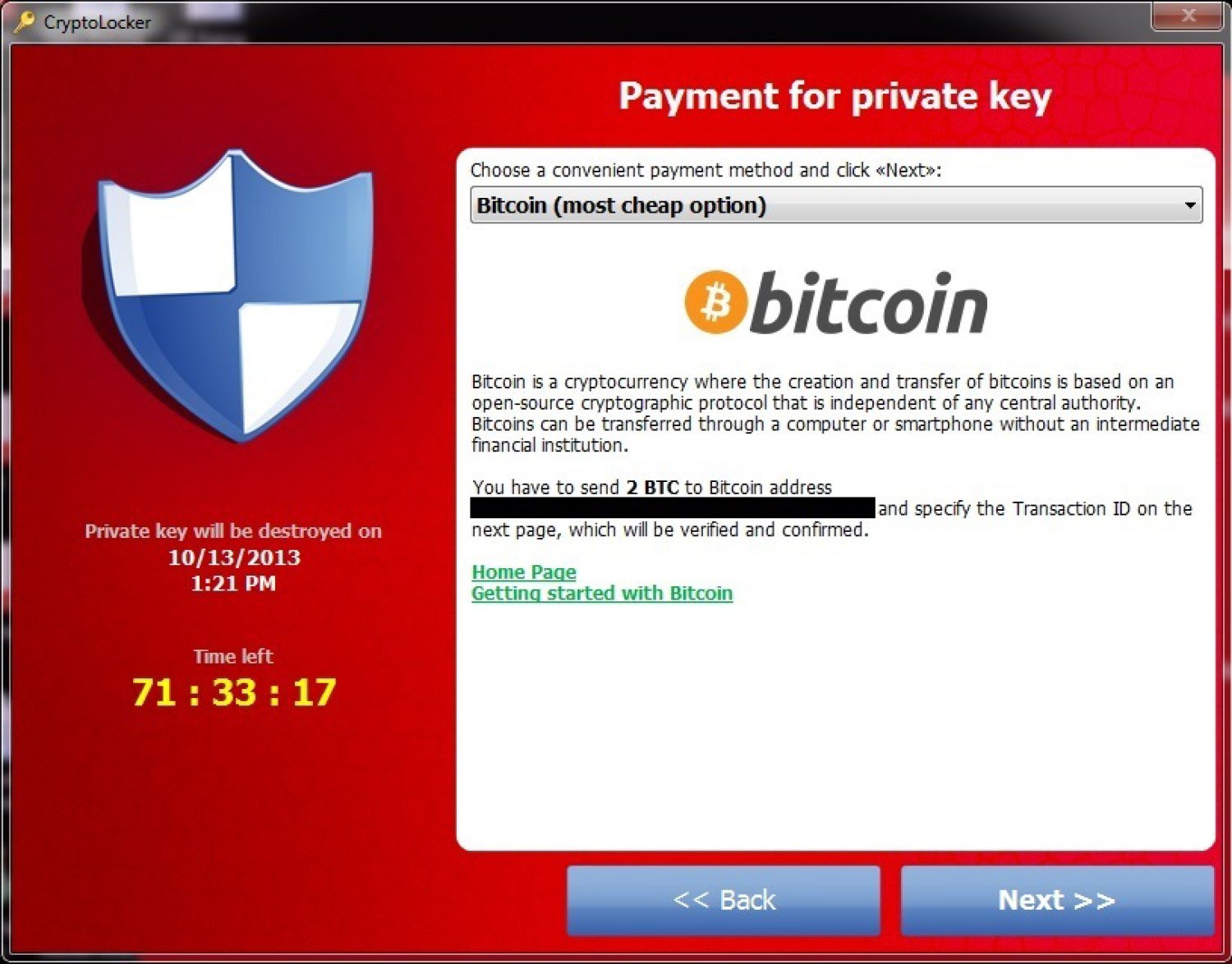
How bad was CryptoLocker?
CryptoLocker is by now a well-known piece of malware that can be especially damaging for any data-driven organization. Once the code has been executed, it encrypts files on desktops and network shares and “holds them for ransom,” prompting any user that tries to open the file to pay a fee to decrypt them.
Who does ransomware target the most?
Construction and property, IT, technology and telecoms, central and federal government, local and state government, lower education, manufacturing and production, financial services. Everyone is a potential ransomware target.
Does ransomware go away if you pay?
While paying the ransom almost always gets you some data back, the percentage of data restored after paying has dropped.
Can ransomware spread through WiFi?
In most cases, ransomware is spread through phishing emails containing malicious attachments or links. However, ransomware can also be spread through other means, such as exploit kits, malvertising, and drive-by downloads.
Is ransomware still a threat
The number of ransomware attacks dropped 15% between 2021 and 2022, according to recent data from Google-owned threat intelligence firm Mandiant.
Cached
What happened to CryptoLocker
CryptoLocker was isolated in late May 2014 via Operation Tovar, which took down the Gameover ZeuS botnet that had been used to distribute the malware.
CachedSimilar
How many people were infected by CryptoLocker
Between September and December 2013, CryptoLocker infected more than 250,000 systems. It earned more than $3 million for its creators before the Gameover ZeuS botnet, which was used to carry out the attacks, was taken offline in 2014 in an international operation.
Cached
What is the target of the CryptoLocker Trojan attack
It is a Trojan horse that infects your computer and then searches for files to encrypt. This includes anything on your hard drives and all connected media — for example, USB memory sticks or any shared network drives. In addition, the malware seeks out files and folders you store in the cloud.
Do I need to worry about ransomware
Ransomware incidents can severely impact business processes and leave organizations without the data they need to operate and deliver mission-critical services.
Should I worry about ransomware
Ransomware is a legitimate risk for anyone with a computer and data they want keep accessible and secure.
Can CryptoLocker be decrypted
Once CryptoLocker encrypts your files, they'll stay encrypted until you decrypt them with the correct key. Removing CryptoLocker prevents it from encrypting anything else, but it isn't going to decrypt your files.
What is the largest ransomware payout
| Summary | Ransom Demanded |
|---|---|
| Colonial Pipeline paid $5 Million ransom one day after cyberattack, CEO tells Senate | $5 Million |
| JBS paid $11 Million to REvil ransomware, $22.5M first demanded | $22.5 Million |
| Insurance giant CNA fully restores systems after ransomware attack | $60 Million |
| REvil gang targets Kaseya | $70 Million |
How bad was CryptoLocker
CryptoLocker is by now a well known piece of malware that can be especially damaging for any data-driven organization. Once the code has been executed, it encrypts files on desktops and network shares and “holds them for ransom”, prompting any user that tries to open the file to pay a fee to decrypt them.
Who does ransomware target the most
Construction and property.IT, technology and telecoms.Central and federal government.Local and state government.Lower education.Manufacturing and production.Financial services.Everyone is a potential ransomware target.
Does ransomware go away if you pay
While paying the ransom almost always gets you some data back, the percentage of data restored after paying has dropped.
Can ransomware spread through WiFi
In most cases, ransomware is spread through phishing emails containing malicious attachments, portable computers, exposure to public WiFi, Zero-Day vulnerabilities, and drive-by downloading.
Should you ever pay ransomware
The realities of ransomware
Law enforcement agencies recommend not paying, because doing so encourages continued criminal activity. In some cases, paying the ransom could even be illegal, because it provides funding for criminal activity.
Is CryptoLocker a Trojan
Cryptolocker Virus Definition
It is a Trojan horse that infects your computer and then searches for files to encrypt. This includes anything on your hard drives and all connected media — for example, USB memory sticks or any shared network drives.
How many computers did CryptoLocker infect
CryptoLocker (2013)
CryptoLocker infected over 500,000 machines for a ransom of $300 or €300. Its most common method of infection was via email attachments – often in innocuous looking documents labelled .
What is the deadliest ransomware
WannaCry ransomware attack
| Screenshot of the ransom note left on an infected system | |
|---|---|
| Date | 12 May 2017 – 15 May 2017 (initial outbreak) |
| Cause | WannaCry worm |
| Outcome | 300,000+ computers infected |
| Arrests | None |
Can you decrypt CryptoLocker
CryptoLocker uses an asymmetric encryption method that makes it difficult to crack. This two-key system uses one public key for encryption and one private key for decryption, each linked to the other. The sender encrypts a file with the public key, and the recipient decrypts it with their private key.
What is the most malicious ransomware
Clop ransomware
Cybercriminals can deploy this malware to infect individuals or entire networks, making it exceedingly dangerous if a company network is infiltrated. Like other types of ransomware, clop encrypts all files on a computer and demands a fee to have it decrypted.
What is the best defense against ransomware
TipsIdentify assets that are searchable via online tools and take steps to reduce that exposure.Protecting Against Ransomware.Understanding Patches and Software Updates.Using Caution with Email Attachments.SMB Security Best Practices.Website Security.Rising Ransomware Threat to Operational Technology Assets.
What are the top 3 ransomware groups
The Most Prolific Ransomware Gangs of 2022LockBit. LockBit had a big year — especially in May when the group was responsible for 40% of all ransomware attacks.REvil.BlackCat (ALPHV)Black Basta.
Why you should not pay ransomware
Paying the first ransom may not solve the issue. If a business decides to comply with the ransom request, the hacker will likely request more money. Even if the hacker provides the encryption keys immediately, it could take the organization weeks or months to restore its encrypted information.
How many percent of ransom paying victims got all their data back
Back then another ransomware report, this time from security vendor Sophos, revealed that 32% of those surveyed opted to pay the ransom but a shocking 92% failed to recover all their data and 29% were unable to recover more than half of the encrypted data.
Does a VPN protect you from ransomware
A VPN can't stop ransomware completely, but it can make you less vulnerable to attacks. With NordVPN (and NordVPN's Threat Protection feature) you're less likely to download malicious files and visit dangerous, malware-ridden websites, so the chances of you being infected with ransomware are lower.
What is the most common way to get infected with ransomware
Ransomware is often spread through phishing emails that contain malicious attachments or through drive-by downloading. Drive-by downloading occurs when a user unknowingly visits an infected website and then malware is downloaded and installed without the user's knowledge.
What is the current average ransomware payout
They threaten to sell or publish that data to coerce an increased ransom payment. Ransom payments increased 144 percent in 2021 over 2020. The average reported ransomware payment in 2022 was $4.7 million.



