What are smart sensors used for?
Summary of the Article
Smart sensors are devices that use embedded microprocessors and wireless communication to monitor, examine, and maintain various systems. They have the ability to collect environmental data accurately with less noise. A smart sensor performs data conversion and digital processing before communicating with external devices. These sensors have various advantages, including self-testing, self-validation, self-adaptation, and self-identification. They also provide real-time data, precision and accuracy, and can work in harsh environments. Smart sensors perform functions such as measurement, configuration, verification, and communication. Examples of smart sensors include temperature sensors, pressure sensors, force sensors, vibration sensors, and humidity sensors. A sensor is a device that detects events or changes in its environment and relays the information to other electronics, typically a computer processor. The main difference between a normal sensor and a smart sensor is that the latter is embedded with a Digital Motion Processor (DMP). A regular sensor does not include a DMP. Smart sensors have both advantages and disadvantages. The complexity and cost of wired smart sensors are higher compared to other types. Additionally, the use of predefined embedded function and the requirement for actuators and external sensor calibration are some drawbacks of smart sensors.
Key Questions about Smart Sensors:
1. What is the purpose of a smart sensor?
A smart sensor enables onboard processing of sensor data, including normalizing the data and filtering noise.
2. Could you explain smart sensors with an example?
Smart sensors use microprocessors and wireless communication to collect accurate environmental data. For example, they can monitor and measure temperature, traffic, and industrial applications.
3. What is the purpose of using sensors?
Sensors detect events or changes in their environment and relay the information to other electronics. They convert physical phenomena into measurable digital signals.
4. What are the advantages of smart sensors?
Smart sensors can self-test, self-validate, self-adapt, and self-identify. They also support real-time decision making and can manage a wide range of conditions.
5. What are the main functions performed by smart sensors?
Smart sensors perform measurement, configuration, verification, and communication functions. They detect physical signals and convert them into electrical signals.
6. What is the difference between a sensor and a smart sensor?
A smart sensor includes a Digital Motion Processor (DMP) and can accept input from external sources. It uses pre-built functions to detect specific combinations of inputs, whereas a regular sensor does not include a DMP.
7. Can you provide a simple example of a sensor?
A Light Dependent Resistor (LDR) is a simple sensor that varies its resistance based on the intensity of light it receives.
8. What are the advantages and disadvantages of smart sensors?
Advantages of smart sensors include real-time data, precision, accuracy, and the ability to work in harsh environments. Disadvantages include higher complexity and cost, required use of predefined embedded function, the need for both actuators and sensors, and management of sensor calibration by an external processor.
9. What are the main types of sensors?
The main types of sensors include position sensors, pressure sensors, temperature sensors, force sensors, vibration sensors, piezo sensors, fluid property sensors, and humidity sensors.
10. What are the advantages of sensors?
Sensors provide real-time data, high precision and accuracy, and can operate in harsh environments.
What is the purpose of a smart sensor
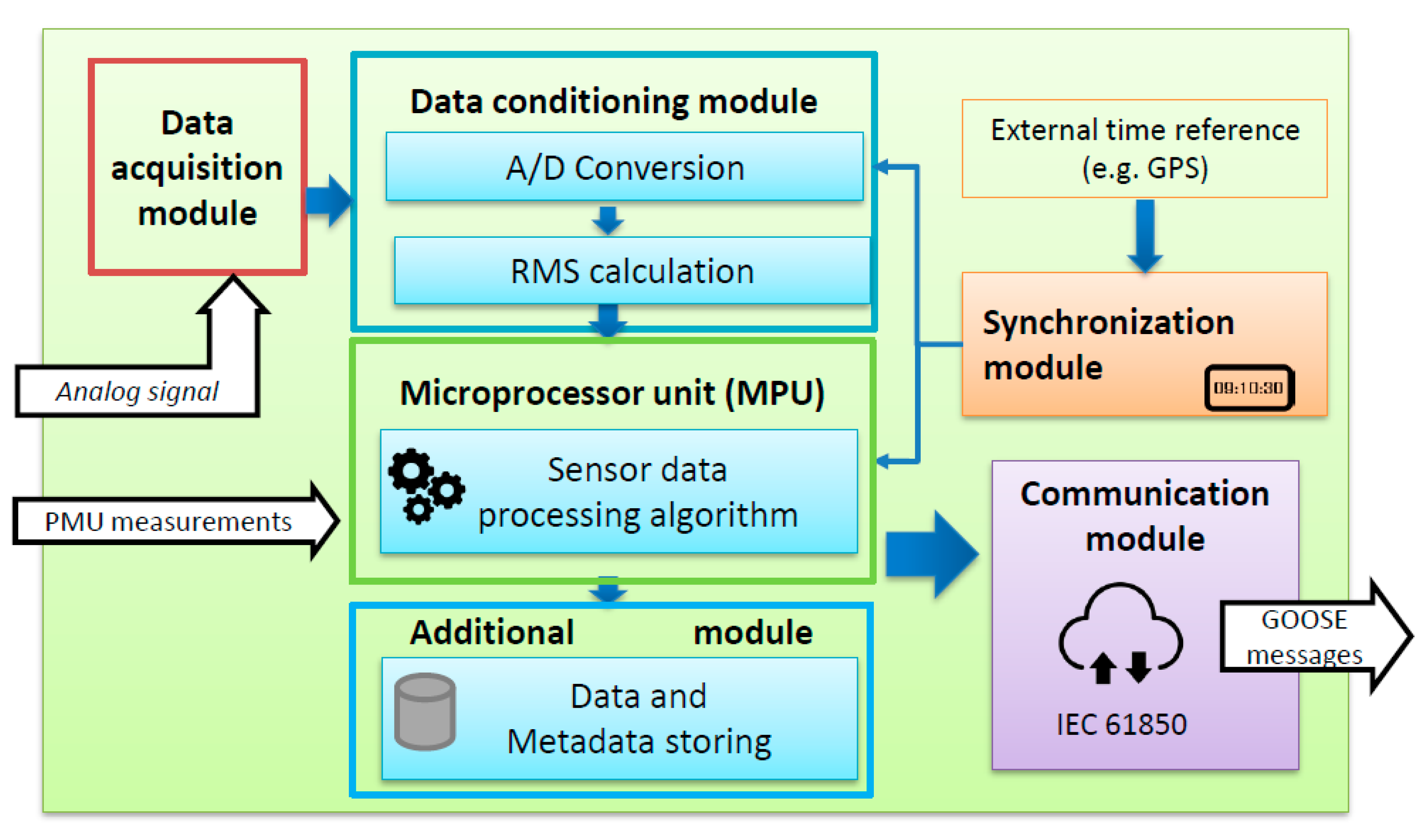
It enables the sensor to perform onboard processing of the sensor data. This might mean normalizing the data, filtering noise or performing other types of signal conditioning. In any case, a smart sensor performs data conversion digital processing prior to any communication to external devices.
What are smart sensors explain with example
Smart sensors are devices that take information from a physical environment and use embedded microprocessors and wireless communication to monitor, examine, and maintain various systems. They have the ability to collect environmental data more accurately with less erroneous noise.
Cached
What is the purpose of using sensors
A sensor is a device, module, machine, or subsystem that detects events or changes in its environment and relays the information to other electronics, most commonly a computer processor. A sensor converts physical phenomena into a measurable digital signal, which can then be displayed, read, or processed further.
What are the advantages of smart sensors
Intelligent sensors are able to carry out a number of intrinsically intelligent functions, such as the ability to self-test, self-validate, self-adapt, and self-identify. They understand process requirements, manage a wide range of conditions, and can detect conditions to support real-time decision making.
What are the 2 things smart sensors check for
These sensors have 4 main functions measurement, configuration, verification & communication. Measurements are simply taken through detecting physical signals & changing them into electrical signals. So this will help in monitoring and measuring things like temperature, traffic, & industrial applications.
What is the difference between a sensor and a smart sensor
The difference between a normal sensor and a smart sensor is that a smart sensor is embedded with a Digital Motion Processor or DMP. A smart sensor can accept input from external sources and use pre-built functions to detect a specific combination of inputs. A regular sensor does not include a DMP.
What is a simple example for sensor
The simplest example of a sensor is an LDR or a Light Dependent Resistor. It is a device, whose resistance varies according to intensity of light it is subjected to. When the light falling on an LDR is more, its resistance becomes very less and when the light is less, well, the resistance of the LDR becomes very high.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of smart sensor
1) In wired smart sensors, complexity is much higher as a consequence the cost is also high. 2) Required use of predefined embedded function during the design of the smart sensor. 3) It requires both actuators and sensors. 4) Sensor calibration has to be managed by an external processor.
What are the 4 main types of sensors
There are many different types of sensors, the main categories are;Position Sensors.Pressure Sensors.Temperature Sensors.Force Sensors.Vibration Sensors.Piezo Sensors.Fluid Property Sensors.Humidity Sensors.
What are 3 advantages of sensors
Sensors have many advantages, including their ability to provide real-time data, their precision and accuracy, and their ability to work in harsh environments.
What can be detected by a sensor
A sensor is a device that detects and responds to some type of input from the physical environment. The input can be light, heat, motion, moisture, pressure or any number of other environmental phenomena.
What types of data can sensors detect
What are examples of sensor data Sensors can be instrumented to track a variety of data points, but the most common include temperature, humidity, pressure, proximity, speed, rotation, light, and gas or chemical levels.
Which does a sensor detect
A sensor is a device that detects and responds to some type of input from the physical environment. The input can be light, heat, motion, moisture, pressure or any number of other environmental phenomena.
How are sensors used in everyday life
all use sensors to monitor oil temperature and pressure, throttle and steering systems and so many more aspects. When you are at work, the lights may turn on using a motion sensor. Public toilet flushes often use a push button or an infrared switch. You may also use a computer which uses many different sensors.
What can sensors detect
A sensor is a device that detects and responds to some type of input from the physical environment. The input can be light, heat, motion, moisture, pressure or any number of other environmental phenomena.
What conditions can a sensor measure
Sensors can be used to measure or detect a vast variety of physical, chemical, and biological quantities, including proteins, bacteria, chemicals, gases, light intensity, motion, position, sound and many others, as shown in Figure 2-1.
What are the pros and cons of sensors
Sensors have many advantages, including their ability to provide real-time data, their precision and accuracy, and their ability to work in harsh environments. However, they also have some disadvantages, including cost, susceptibility to interference and damage, and limited lifespan.
How does a sensor detect a person
Area reflective sensors emit infrared rays from an LED and use the reflection of those rays to measure the distance to the person or object, allowing for detection when the subject moves within the designated area.
What are examples of data collected by sensors
What are examples of sensor data Sensors can be instrumented to track a variety of data points, but the most common include temperature, humidity, pressure, proximity, speed, rotation, light, and gas or chemical levels.
What sensors can detect people
These include software technologies such CAPTCHA and reCAPTCHA, as well as hardware technologies such as:Radar technology.Image recognition of human shapes.Security switch.Fingerprint sensors.Infrared detectors.Acoustic sensors.Vibration sensors.
Where are sensors mostly used
The sensors are used in a wide range of industries and settings, including agriculture, manufacturing, data centers, meteorology, and heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC). Level. A level sensor can determine the level of a physical substance such as water, fuel, coolant, grain, fertilizer or waste.
How can you tell if someone is a sensor
Some easy ways to identify a sensor or an intuitive:
– Sensors prefer to talk about what is happening or what has happened. They are more concerned with the details and will have more descriptive or literal details in their conversation. – Intuitives prefer to talk about what things “mean” or symbolize.
What are the disadvantages of smart sensors
Application disadvantages of smart sensors:R&D time and costs are required.The production process is more complicated.Maintenance costs are high.Power consumption considerations.If connected to the Internet, network stability needs to be considered.
What is the main disadvantage of sensor
In conclusion, sensors are powerful devices that have many advantages, such as providing real-time data, high precision, and working in harsh environments. However, they also have some disadvantages, such as high costs, susceptibility to interference and damage, and limited lifespan.
Which sensor detect human activity
The sensors embedded in these lightweight devices can unobtrusively quantify activities of daily living and provide long-term objective, insightful measures for HAR applications. Among them, accelerometers and gyroscopes are the two most common sensors that are adopted for human activity recognition.



