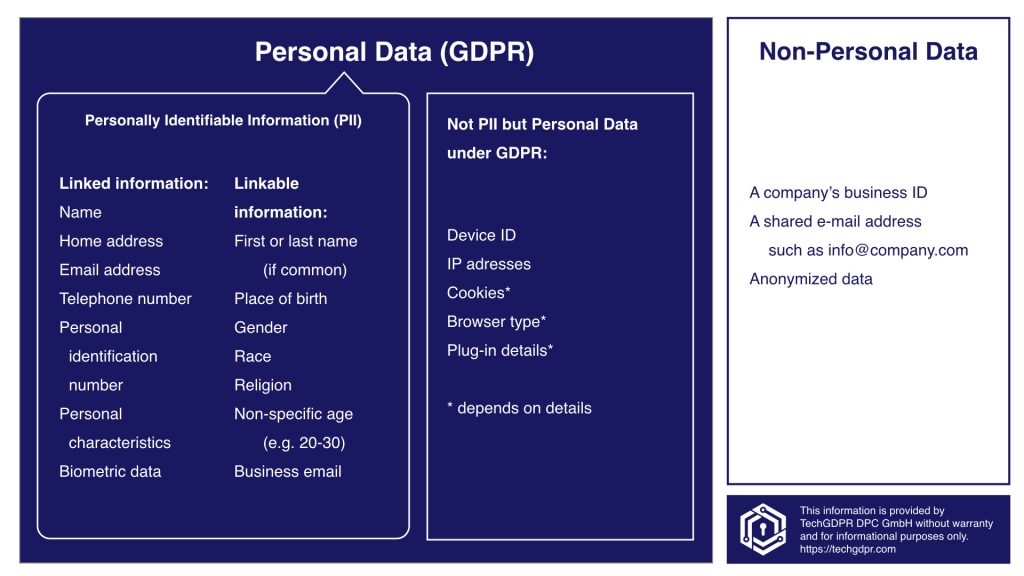
What counts as PII under GDPR?
First and foremost, let’s clarify what Personally Identifiable Information (PII) means according to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). PII refers to a limited scope of data that includes personal details such as name, address, birth date, Social Security numbers, and banking information. However, the GDPR goes beyond traditional PII and also considers other data as personal information. This includes photographs, social media posts, preferences, and location.
Now, let’s take a look at some key questions and detailed answers related to PII under the GDPR:
1. What is considered PII under the GDPR?
According to the GDPR, PII refers to personal information that can be used to identify an individual. This includes traditional PII like name, address, birth date, Social Security numbers, and banking information. Additionally, personal information in the GDPR context also encompasses data such as photographs, social media posts, preferences, and location.
2. What can be classified as PII?
PII can be classified as any information about an individual that can be used to distinguish or trace their identity. This includes not only traditional PII but also other data such as biometric records and more.
3. What are examples of PII according to GDPR guidelines?
Some examples of PII as per GDPR guidelines include names, addresses, financial information, login IDs, biometric identifiers, video footage, geographic location data, and customer loyalty histories.
4. Which 5 types of information are examples of PII?
The five types of information that are considered as examples of PII include full name, home address, email address, social security number, passport number, driver’s license number, credit card numbers, and date of birth.
5. What is not considered as PII?
While PII refers to sensitive data that can be used to identify an individual, there are certain types of information that are not considered as PII. Examples of non-PII include business phone numbers, race, religion, gender, workplace, and job titles.
6. What is not PII (personally identifiable information)?
Non-personally identifiable information (non-PII) refers to data that cannot be used on its own to trace or identify a person. This can include aggregated statistics on the use of a product or service.
7. What is not considered PII?
As mentioned earlier, non-PII includes business phone numbers, race, religion, gender, workplace, and job titles. However, it is important to note that although this information may not be considered PII on its own, it should still be treated as sensitive and linkable information when combined with other data.
8. What is not considered PII data?
Similar to the previous question, non-PII data includes information like business phone numbers, race, religion, gender, workplace, and job titles. While this data may not fall under the category of PII on its own, it could still potentially identify an individual when combined with other data.
9. What are 5 examples of PII?
Five examples of PII include a social security number (SSN), passport number, driver’s license number, taxpayer identification number, financial account number, and credit card number. These personal identification numbers are considered as PII under the GDPR.
10. What information is not considered PII?
Again, information such as business phone numbers, race, religion, gender, workplace, and job titles are typically not considered PII. However, it is crucial to treat these types of information as sensitive and potentially linkable because they could still identify an individual when combined with other data.
11. Which is not categorized as PII data?
Non-PII data typically includes data collected by browsers and servers using cookies. Examples of non-PII data include device type, browser type, plugin details, language preference, time zone, and screen size.
These questions and answers provide a better understanding of what constitutes PII and what falls outside the scope of PII under the GDPR. It is important to adhere to the regulations and protect individuals’ personal information while handling data.
What is considered PII under the GDPR
PII has a limited scope of data which includes: name, address, birth date, Social Security numbers and banking information. Whereas, personal information in the context of the GDPR also references data such as: photographs, social media posts, preferences and location as personal.
What can be classified as PII
Personally Identifiable Information (PII) Data is any information about an individual maintained by a Unit, including (1) any information that can be used to distinguish or trace an individual's identity, such as name, social security number, date and place of birth, mother's maiden name, or biometric records; and (2) …
What are examples of PII as per GDPR guidelines
What Is Considered PII Under the GDPRNames.Addresses.Financial information.Login IDs.Biometric identifiers.Video footage.Geographic location data.Customer loyalty histories.
Cached
Which 5 types of information are examples of PII
What pieces of information are considered PIIFull name.Home address.Email address.Social security number.Passport number.Driver's license number.Credit card numbers.Date of birth.
What is not considered as PII
PII, or personally identifiable information, is sensitive data that could be used to identify, contact, or locate an individual. What are some examples of non-PII Info such as business phone numbers and race, religion, gender, workplace, and job titles are typically not considered PII.
What is not PII personally identifiable information
Non-personally identifiable information (non-PII) is data that cannot be used on its own to trace, or identify a person. Examples of non-PII include, but are not limited to: Aggregated statistics on the use of product / service.
What is not considered PII
PII, or personally identifiable information, is sensitive data that could be used to identify, contact, or locate an individual. What are some examples of non-PII Info such as business phone numbers and race, religion, gender, workplace, and job titles are typically not considered PII.
What is not considered PII data
PII, or personally identifiable information, is sensitive data that could be used to identify, contact, or locate an individual. What are some examples of non-PII Info such as business phone numbers and race, religion, gender, workplace, and job titles are typically not considered PII.
What are 5 examples of PII
Personal identification numbers: social security number (SSN), passport number, driver's license number, taxpayer identification number, patient identification number, financial account number, or credit card number.
What information is not considered PII
Info such as business phone numbers and race, religion, gender, workplace, and job titles are typically not considered PII. But they should still be treated as sensitive, linkable info because they could identify an individual when combined with other data.
Which is not Categorised as PII data
Non-PII data typically includes data collected by browsers and servers using cookies. Device type, browser type, plugin details, language preference, time zone, screen size are few examples of non PII data.
What is considered PII but not Phi
Protected Health Information (PHI) is any health information that includes any of the 18 elements identified by HIPAA. Personally Identifiable Information (PII) is defined as data used in research that is not considered PHI and is therefore not subject to the HIPAA Privacy and security Rules.
What data has no PII
Non-personally identifiable information (non-PII) is data that cannot be used on its own to trace, or identify a person. Examples of non-PII include, but are not limited to: Aggregated statistics on the use of product / service.
What is considered PII but not PHI
Protected Health Information (PHI) is any health information that includes any of the 18 elements identified by HIPAA. Personally Identifiable Information (PII) is defined as data used in research that is not considered PHI and is therefore not subject to the HIPAA Privacy and security Rules.
What does PII not include
Non-personally identifiable information (non-PII) is data that cannot be used on its own to trace, or identify a person. Examples of non-PII include, but are not limited to: Aggregated statistics on the use of product / service. Partially or fully masked IP addresses.
What is an example of a PII and a non-PII
PII, or personally identifiable information, is sensitive data that could be used to identify, contact, or locate an individual. What are some examples of non-PII Info such as business phone numbers and race, religion, gender, workplace, and job titles are typically not considered PII.
What are 3 examples of information that is not considered PHI
Examples of health data that is not considered PHI: Number of steps in a pedometer. Number of calories burned. Blood sugar readings w/out personally identifiable user information (PII) (such as an account or user name)
What sensitive data is not PII
The two main types of PII are sensitive PII and non-sensitive PII. Sensitive PII, such as your driver's license or Social Security number, can directly reveal your identity. Non-sensitive PII includes information that could be in a public record, like your birthday or phone number.
What are the 18 identifiers of PHI
18 HIPAA Identifiers for PHIPatient names.Geographical elements (such as a street address, city, county, or zip code)Dates related to the health or identity of individuals (including birthdates, date of admission, date of discharge, date of death, or exact age of a patient older than 89)Telephone numbers.Fax numbers.
What information can be shared without violating HIPAA
What information can be shared without violating HIPAA All information can be shared without violating HIPAA provided it is shared for a permissible use or disclosure or the entity sharing the information has obtained a written authorization from the subject of the information.
What is not included in PII
Non-PII data typically includes data collected by browsers and servers using cookies. Device type, browser type, plugin details, language preference, time zone, screen size are few examples of non PII data.
What is the difference between PII and personal information
From a zoomed-out perspective, the greatest difference between personal data and PII is that PII is often used to differentiate one person from another, while personal data includes any information related to a living individual, whether it distinguishes them from another individual or not.
What identifiers are not considered PHI
What is not PHI De-identified health information neither identifies nor provides a reasonable base to identify an individual. Health information by itself without the 18 identifiers is not considered to be PHI. For example, a dataset of vital signs by themselves do not constitute protected health information.
What health information is not protected by HIPAA
What is not PHI De-identified health information neither identifies nor provides a reasonable base to identify an individual. Health information by itself without the 18 identifiers is not considered to be PHI. For example, a dataset of vital signs by themselves do not constitute protected health information.
What information is exempt from HIPAA
Exceptions to the HIPAA Privacy Rule
This would include purposes such as quality assurance, utilization review, credentialing, and other activities that are part of ensuring appropriate treatment and payment. Limitations apply to uses and disclosures for the purpose of facilitating another party's activities.



