What is checked on a credit report?
Summary of the article
Your credit reports include information about the types of credit accounts you’ve had, your payment history, and certain other information such as your credit limits. Credit reports from Equifax, TransUnion, and Experian may contain different account information. As part of a credit check, companies may look at whether you’ve paid back your credit on time, how much credit you currently have, and how you’re managing it. They may also look at any financial associations you may have and what their credit history is.
If you have late or missed payments, defaults, or county court judgments in your credit history, it may fail a credit check. Having an Individual Voluntary Agreement or Debt Management Plan might suggest that you can’t afford any more debt at the moment. Your credit report does show all your debt, including listing all of your past and current credit accounts, payment history, loan amounts, bankruptcies, foreclosures, and current balances.
Red flags on a credit report are patterns, practices, or activities that indicate a possibility of identity theft. These flags produce a three-digit score that calculates the customer’s fraud risk through the credit report. Five things found on a credit report are personal information, credit history, credit inquiries, public records, and sometimes a personal statement. You can get a free credit report each year from the three credit reporting agencies: Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion.
Bank transactions and account balances are not reported to the national credit bureaus and do not appear on your credit reports. However, unpaid bank fees or penalties turned over to collection agencies will appear and hurt your credit scores. Hard inquiries, missing payments, and maxing out a card can knock down your credit score. Arrears, missed, late, or defaulted payments reported by lenders and service providers can also negatively affect your credit score. It is not true that your credit is automatically cleared after 7 years.
Questions and Answers
1. What shows up on your credit report?
Your credit reports include information about the types of credit accounts you’ve had, your payment history, and certain other information such as your credit limits. Credit reports from the three nationwide consumer reporting agencies — Equifax, TransUnion, and Experian — may contain different account information.
2. What do they check in a credit check?
As part of a credit check, companies may look at whether you’ve paid back your credit on time, how much credit you currently have, and how you’re managing it. They may also look at any financial associations you may have (such as someone you share a bank account or mortgage with) and what their credit history is.
3. What will fail a credit check?
You may fail a credit check if you have late or missed payments, defaults, or county court judgments in your credit history. Having an Individual Voluntary Agreement or Debt Management Plan might also suggest that you can’t afford any more debt at the moment.
4. Does my credit report show all my debt?
Yes, your credit report shows all of your past and current credit accounts, along with the dates they were opened and closed. It also shows lenders your payment history, the amount of every loan you’ve taken out, any past bankruptcies or foreclosures, and your current balances.
5. What are red flags on a credit report?
Red flags are patterns, practices, or activities that indicate a possibility of identity theft. These flags produce a three-digit score that calculates the customer’s fraud risk through the credit report. A higher score indicates a lower risk of identity fraud.
6. What are 5 things found on a credit report?
The information contained incredit reports can be categorized into 4-5 groups: personal information, credit history, credit inquiries, public records, and sometimes a personal statement.
7. What are the 3 major credit checks?
By law, you can get a free credit report each year from the three credit reporting agencies: Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion.
8. Does a credit check show your bank balance?
Bank transactions and account balances are not reported to the national credit bureaus and do not appear on your credit reports. However, unpaid bank fees or penalties turned over to collection agencies will appear and hurt your credit scores.
9. What knocks down your credit score?
Hard inquiries, missing payments, and maxing out a card can hurt your credit score. There are also other mistakes that can significantly lower it.
10. What badly affects credit score?
Arrears, missed, late, or defaulted payments reported by lenders and service providers can negatively affect your credit score. This is not limited to mortgage, credit card, loan, car finance, and overdraft payments.
11. Is it true that after 7 years your credit is clear?
No, it is not true that your credit is automatically cleared after 7 years. Negative items may still remain on your credit report after this period.
What shows up on your credit report
Your credit reports include information about the types of credit accounts you've had, your payment history and certain other information such as your credit limits. Credit reports from the three nationwide consumer reporting agencies — Equifax, TransUnion and Experian — may contain different account information.
Cached
What do they check in a credit check
As part of a credit check, companies may look at whether you've paid back your credit on time, how much credit you currently have and how you're managing it. They may also look at any financial associations you may have (such as someone you share a bank account or mortgage with) and what their credit history is.
What will fail a credit check
You have late or missed payments, defaults, or county court judgments in your credit history. These may indicate you've had trouble repaying debt in the past. You have an Individual Voluntary Agreement or Debt Management Plan. This might suggest that you can't afford any more debt at the moment.
Does my credit report show all my debt
As well as listing all of your past and current credit accounts, along with the dates they were opened and closed, credit reports also show lenders your payment history, the amount of every loan you've ever taken out, any past bankruptcies or foreclosures — and your current balances.
What are red flags on credit report
A red flag is a pattern, practice, or activity that indicates a possibility of identity theft. These flags produce a three digit score (0-999) that calculates the customer's fraud risk through the credit report. A higher score indicates a lower risk of identity fraud.
What are 5 things found on a credit report
The information that is contained in your credit reports can be categorized into 4-5 groups: 1) Personal Information; 2) Credit History; 3) Credit Inquiries; 4) Public Records; and, sometimes, 5) a Personal Statement. These sections are explained in further detail below.
What are the 3 major credit checks
By law, you can get a free credit report each year from the three credit reporting agencies (CRAs). These agencies include Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion.
Does a credit check show your bank balance
Bank transactions and account balances are not reported to the national credit bureaus and do not appear on your credit reports—but unpaid bank fees or penalties turned over to collection agencies will appear on your credit reports and hurt your credit scores.
What knocks down your credit score
Hard inquiries, missing a payment and maxing out a card hurt your credit score. But there are other mistakes that can really tank it. Here's what to avoid. The content on this page is accurate as of the posting date; however, some of our partner offers may have expired.
What badly affects credit score
Lenders and other service providers report arrears, missed, late or defaulted payments to the credit reference agencies, which may impact your credit score. This isn't limited to mortgage, credit card, loan, car finance and overdraft payments.
Is it true that after 7 years your credit is clear
Most negative items should automatically fall off your credit reports seven years from the date of your first missed payment, at which point your credit scores may start rising. But if you are otherwise using credit responsibly, your score may rebound to its starting point within three months to six years.
What counts towards total debt
Total debt includes long-term liabilities, such as mortgages and other loans that do not mature for several years, as well as short-term obligations, including loan payments, credit cards, and accounts payable balances.
What are some of the warning signs of bad credit
Six Warning Signs of Poor CreditDefaulted on several debt payments.Rejected loan application.Credit card issuer rejects or closes your credit card.Debt collection agency contacts you.Difficulty getting a job.Difficulty getting an apartment to rent.
What are covered accounts red flags
The Red Flag Rule stipulates that any financial institution or creditor must evaluate whether any new or existing accounts are considered “covered accounts” by the regulations. Covered accounts are described as those that are typically used by individuals and households to facilitate multiple transactions.
What are 5 things not in your credit score
However, they do not consider: Your race, color, religion, national origin, sex and marital status. US law prohibits credit scoring from considering these facts, as well as any receipt of public assistance, or the exercise of any consumer right under the Consumer Credit Protection Act.
What are 3 things you might find on a credit report
Credit accountsCurrent and historical credit accounts, including the type of account (mortgage, installment, revolving, etc.)The credit limit or amount.Account balance.Account payment history.The date the account was opened and closed.The name of the creditor.
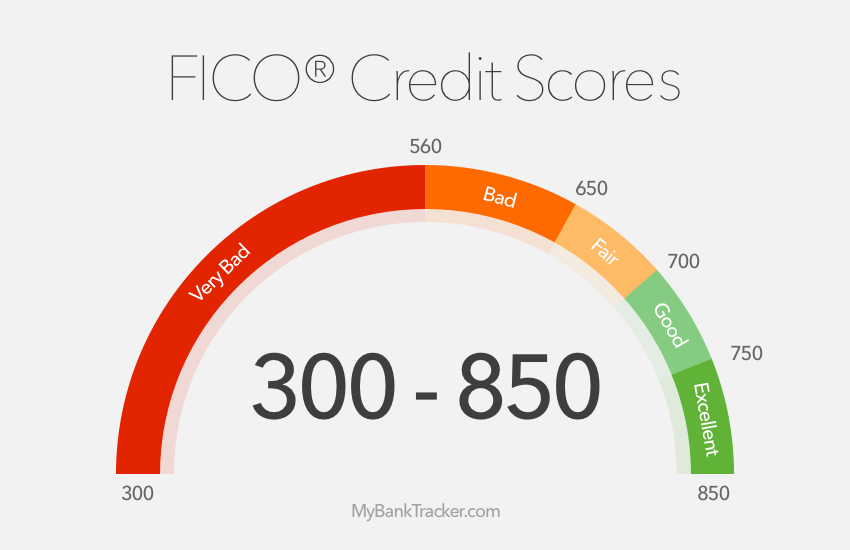
Which credit score is the hardest
Here are FICO's basic credit score ranges:Exceptional Credit: 800 to 850.Very Good Credit: 740 to 799.Good Credit: 670 to 739.Fair Credit: 580 to 669.Poor Credit: Under 580.
What is the most commonly checked credit score
FICO 8
FICO 8 is still the most widely used credit score today. If you apply for a credit card or personal loan, odds are that the lender will check your FICO 8 score. FICO 8 is unique in its treatment of factors such as credit utilization, late payments, and small-balance collection accounts.
What has biggest impact on credit score
Payment History
1. Payment History: 35% Your payment history carries the most weight in factors that affect your credit score, because it reveals whether you have a history of repaying funds that are loaned to you. This component of your score considers the following factors:3.
What are 3 things that hurt your credit score
10 Things That Can Hurt Your Credit ScoreGetting a new cell phone.Not paying your parking tickets.Using a business credit card.Asking for a credit limit increase.Closing an unused credit card.Not using your credit cards.Using a debit card to rent a car.Opening an account at a new financial institution.
What hurts credit score the most
1. Payment History: 35% Your payment history carries the most weight in factors that affect your credit score, because it reveals whether you have a history of repaying funds that are loaned to you.
What brings up your credit score the most
One of the best things you can do to improve your credit score is to pay your debts on time and in full whenever possible. Payment history makes up a significant chunk of your credit score, so it's important to avoid late payments.
How long until your credit history is wiped
Generally speaking, negative information such as late or missed payments, accounts that have been sent to collection agencies, accounts not being paid as agreed, or bankruptcies stays on credit reports for approximately seven years.
Does an unpaid debt ever go away
A debt doesn't generally expire or disappear until its paid, but in many states, there may be a time limit on how long creditors or debt collectors can use legal action to collect a debt.
What is excluded from total debt
It should be noted that the total debt measure does not include short-term liabilities such as accounts payable and long-term liabilities such as capital leases and pension plan obligations.



