What is passive sensor and active sensor?
Summary
Sensors can be classified into two main categories: active and passive. Active sensors emit energy and measure the reflected or scattered signal, while passive sensors detect the natural radiation or emission from the target or the environment.
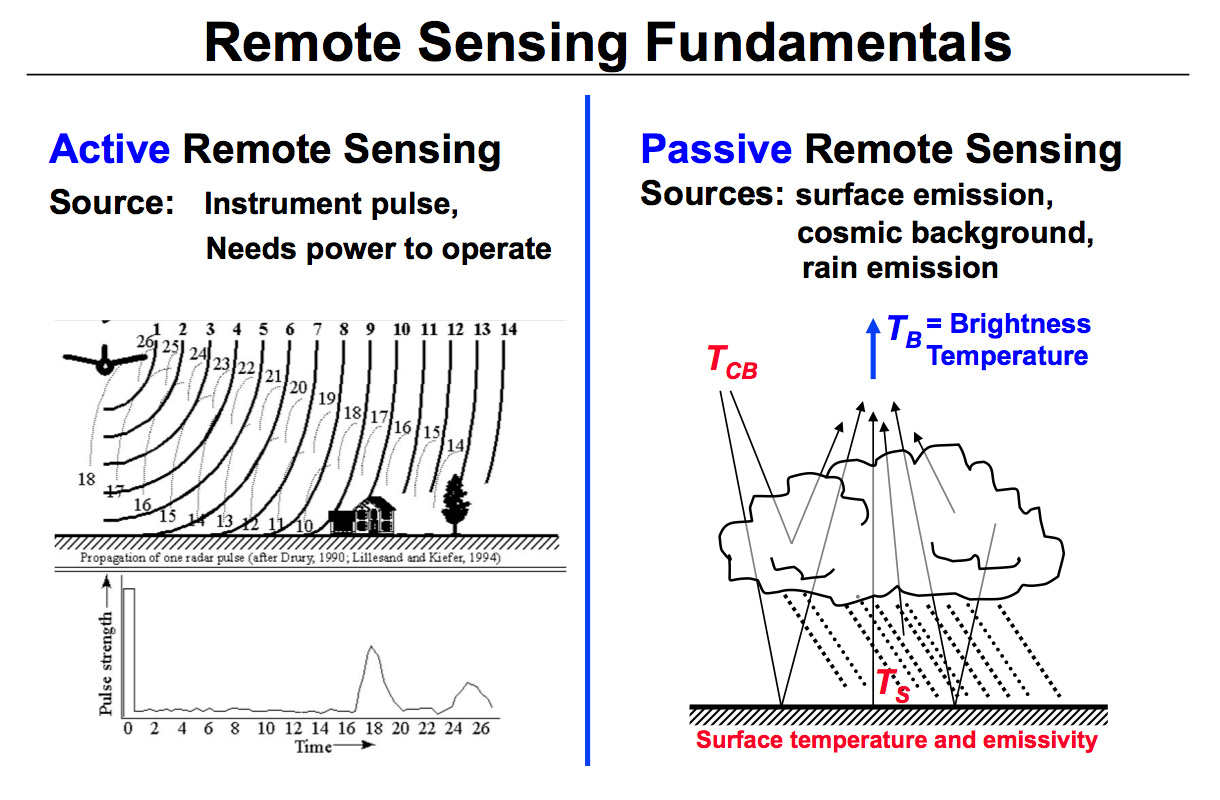
Active sensors send out a pulse of energy and detect the changes in the return signal. Most active sensors operate in the microwave portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, which makes them able to penetrate the atmosphere under most conditions.
The difference between active and passive remote sensing sensors is that active remote sensing instruments operate with their own source of emission or light, while passive ones rely on the reflected one. Radiation also differs by wavelengths that fall into short (visible, NIR, MIR) and long (microwave).
Examples of other active sensor-based technologies include scanning electron microscopes, LiDAR, radar, GPS, x-ray, sonar, infrared, and seismic.
In the active voice, the sentence’s subject performs the action on the action’s target. In the passive voice, the target of the action is the main focus, and the verb acts upon the subject.
A passive sensor is one which just ‘listens’ to what is happening. Examples include a light sensor which detects if a light is shining on it, and an infra-red sensor which detects the temperature of an object.
Some examples of active sensors are a laser fluorosensor and a synthetic aperture radar (SAR).
RADAR and LiDAR are examples of active remote sensing where the time delay between emission and return is measured, establishing the location, speed, and direction of an object. Passive sensors gather radiation that is emitted or reflected by the object or surrounding areas.
Advantages of active sensors over passive sensors include their independence from sunlight and the ability to retrieve information about the Earth’s surface at night. Additionally, active sensors can be weather independent depending on the considered wavelength.
Passive sensor examples include an accelerometer, which measures acceleration, and a hyperspectral radiometer, which detects narrow spectral bands throughout the electromagnetic spectrum.
Questions and Answers
1. What is passive and active sensor?
Sensors can be classified into two main categories: active and passive. Active sensors emit energy and measure the reflected or scattered signal, while passive sensors detect the natural radiation or emission from the target or the environment.
2. What is a passive sensor?
A passive sensor is a microwave instrument designed to receive and measure natural emissions produced by constituents of the Earth’s surface and its atmosphere.
3. What is an active sensor?
Active sensors send out a pulse of energy and detect the changes in the return signal. Most active sensors operate in the microwave portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, which makes them able to penetrate the atmosphere under most conditions.
4. What is the difference between active and passive remote sensing sensors?
The difference between active and passive remote sensing sensors is that active remote sensing instruments operate with their own source of emission or light, while passive ones rely on the reflected one. Radiation also differs by wavelengths that fall into short (visible, NIR, MIR) and long (microwave).
5. What are three examples of active sensors?
Examples of other active sensor-based technologies include scanning electron microscopes, LiDAR, radar, GPS, x-ray, sonar, infrared, and seismic.
6. What is the difference between active and passive?
In the active voice, the sentence’s subject performs the action on the action’s target. In the passive voice, the target of the action is the main focus, and the verb acts upon the subject.
7. What is a simple example of a passive sensor?
A passive sensor is one which just ‘listens’ to what is happening. Examples include a light sensor which detects if a light is shining on it and an infra-red sensor which detects the temperature of an object.
8. What are two examples of active sensors?
Some examples of active sensors are a laser fluorosensor and a synthetic aperture radar (SAR).
9. What are examples of active and passive remote sensors?
RADAR and LiDAR are examples of active remote sensing where the time delay between emission and return is measured, establishing the location, speed, and direction of an object. Passive sensors gather radiation that is emitted or reflected by the object or surrounding areas.
10. What are the advantages of active sensors over passive sensors?
Advantages of active sensors over passive sensors include their independence from sunlight and the ability to retrieve information about the Earth’s surface at night. Additionally, active sensors can be weather independent depending on the considered wavelength.
11. What are passive sensor examples?
Passive sensor examples include an accelerometer, which measures acceleration, and a hyperspectral radiometer, which detects narrow spectral bands throughout the electromagnetic spectrum.
What is passive and active sensor
Sensors can be classified into two main categories: active and passive. Active sensors emit energy and measure the reflected or scattered signal, while passive sensors detect the natural radiation or emission from the target or the environment.
What is a passive sensor
Passive Sensors
A passive sensor is a microwave instrument designed to receive and to measure natural emissions produced by constituents of the Earth's surface and its atmosphere.
CachedSimilar
What is active sensor
Active sensors send out a pulse of energy and detect the changes in the return signal. Most active sensors operate in the microwave portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, which makes them able to penetrate the atmosphere under most conditions.
What is the difference between active and passive remote sensing sensors
passive. Active remote sensing instruments operate with their own source of emission or light, while passive ones rely on the reflected one. Radiation also differs by wavelengths that fall into short (visible, NIR, MIR) and long (microwave). Radars and lidars are the most epic examples of active remote sensing.
Cached
What are 3 examples of active sensors
Examples of other active sensor-based technologies include: scanning electron microscopes, LiDAR, radar, GPS, x-ray, sonar, infrared and seismic.
What is difference between active and passive
In the active voice, the sentence's subject performs the action on the action's target. In the passive voice, the target of the action is the main focus, and the verb acts upon the subject.
What is a simple example of passive sensor
A passive sensor is one which just 'listens' to what is happening. Examples include: A light sensor which detects if a light is shining on it. An infra-red sensor which detects the temperature of an object.
What are two examples of active sensors
Some examples of active sensors are a laser fluorosensor and a synthetic aperture radar (SAR).
What are examples of active and passive remote sensors
RADAR and LiDAR are examples of active remote sensing where the time delay between emission and return is measured, establishing the location, speed and direction of an object. Passive sensors gather radiation that is emitted or reflected by the object or surrounding areas.
What are the advantages of active sensors over passive sensors
As active sensors produce their own radiation and do not rely on e.g. Sun radiation, they are daytime independent and can also retrieve information about the Earth's surface by night. Furthermore, depending of the considered wavelength, active sensors are weather independent.
What are passive sensors examples
Passive SensorsAccelerometer—An instrument that measures acceleration (change in velocity per unit time).Hyperspectral radiometer—An advanced multispectral sensor that detects hundreds of very narrow spectral bands throughout the visible, near-infrared, and mid-infrared portions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
What is active and passive with example
Examples of Active and Passive Voice
Active- He loves me. Passive- I am loved by him. The subject of the active voice example above is "he," the verb is "loves," and the object is "me." The subject of the passive voice phrase is "I," the verb is "am loved," and the object is "him."
What are two differences between active and passive
Active transport requires energy for the movement of molecules whereas passive transport does not require energy for the movement of molecules. In active transport, the molecules move against the concentration gradient whereas in passive transport, the molecules move along the concentration gradient.
What are the 2 classifications of sensors
Classification of Sensors
In the first classification of the sensors, they are divided in to Active and Passive. Active Sensors are those which require an external excitation signal or a power signal. Passive Sensors, on the other hand, do not require any external power signal and directly generates output response.
What is an example of a passive sensor in a car
Airbags, Seatbelts, Whiplash Protection System etc. are common Passive Safety Systems deployed in vehicles these days.
Where are passive sensors used
Passive sensors detect energy emitted or reflected from an object, and include different types of radiometers and spectrometers. Most passive systems used in remote sensing applications operate in the visible, infrared, thermal infrared, and microwave portions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
What are the advantages of active and passive
Using active voice often improves clarity, while passive voice can help avoid unnecessary repetition. Active voice can help ensure clarity by making it clear to the reader who is taking action in the sentence.
What’s the difference between active and passive
In the active voice, the sentence's subject performs the action on the action's target. In the passive voice, the target of the action is the main focus, and the verb acts upon the subject.
What is passive and its example
A verb is in the passive voice when the subject of the sentence is acted on by the verb. For example, in “The ball was thrown by the pitcher,” the ball (the subject) receives the action of the verb, and was thrown is in the passive voice.
What is an example of active vs passive
Active voice: Jerry knocked over the lamp. Passive voice: The lamp was knocked over by Jerry. Both sentences describe the same action taking place—Jerry making contact with a lamp and causing it to fall over—with the first sentence making Jerry the subject and the second making the lamp the subject.
Which is better passive or active
In writing, always consider whether you should use the passive or active voice. It will depend on what you, the writer, want to convey: if you want to draw attention to the doer, use the passive voice; if your intent is to put the focus on the action, then you should go for the active voice.
What are different types of sensors
Types of Sensors/Detectors/Transducers
Sensor types are common among many of the various subcategories. For example, Hall effect sensors are found in proximity sensors, level sensors, motion sensors, and so on. Infrared sensors are used for level sensing, flame detection, etc.
What is different types of different types of sensor
All types of sensors can be basically classified into analog sensors and digital sensors. But, there are a few types of sensors such as temperature sensors, IR sensors, ultrasonic sensors, pressure sensors, proximity sensors, and touch sensors are frequently used in most electronics applications.
What is an example of an active sensor in a car
Automotive sensors fall into two categories: active and passive sensors. Active sensors send out energy in the form of a wave and look for objects based upon the information that comes back. One example is radar, which emits radio waves that are returned by reflective objects in the path of the beam.
What is the main difference between active and passive
The active voice asserts that the person or thing represented by the grammatical subject performs the action represented by the verb. The passive voice makes the subject the person or thing acted on or affected by the action represented by the verb.



