What is rip networking?
Summary of the Article:
OSPF stands for Open Shortest Path First and is a link-state routing protocol, while RIP stands for Routing Information Protocol and is a distance-vector routing protocol. OSPF uses cost as its metric when deciding which route to take, while RIP uses hop count as its metric.
RIP will automatically summarize routes to the classful boundary by default. For example, if you’ve got an interface with IP address 192.168.10.1/30, and under RIP you include that with a network statement, it will be advertised as 192.168.10.0/24.
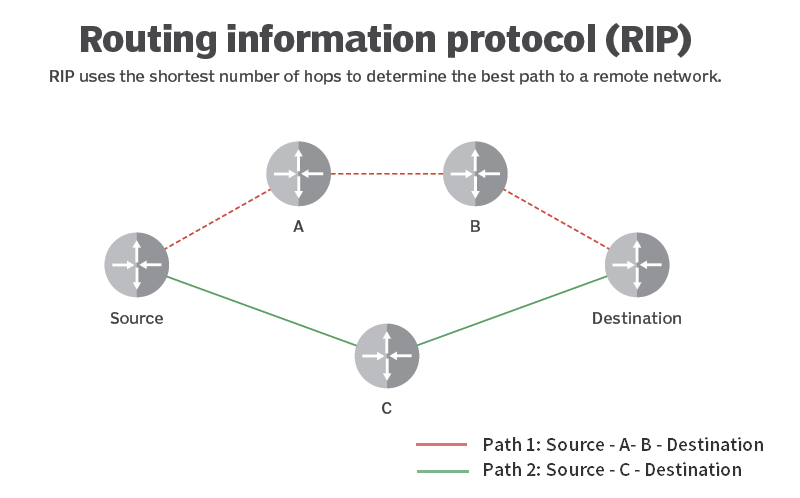
The RIP IGP uses the Bellman-Ford, or distance-vector, algorithm to determine the best route to a destination. RIP uses the hop count as the metric. RIP enables hosts and routers to exchange information for computing routes through an IP-based network.
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is normally a broadcast protocol, and for RIP routing updates to reach nonbroadcast networks, you must configure the Cisco software to permit this exchange of routing information.
OSPF routing protocol has complete knowledge of network topology, allowing routers to calculate routes based on incoming requests. OSPF protocol has no limitations in hop count, unlike RIP protocol that has only 15 hops at most. So OSPF converges faster than RIP and has better load balancing.
OSPF and RIP are Interior Gateway Protocols (IGP) and distribute routing information within an autonomous system, whereas BGP is an Exterior Gateway Protocol. The routes learned via the dynamic routing protocols are applied to the kernel routing table.
It became ubiquitous on headstones in the 18th century and is widely used today when mentioning someone’s death.
This is one of the biggest disadvantages of RIP. Bandwidth utilization in RIP is very high as it broadcasts its updates every 30 seconds. RIP supports only 15 hop count, so a maximum of 16 routers can be configured in RIP. Here the convergence rate is slow.
After comparing RIP vs OSPF differences, it’s clear that RIP protocol is ideal for small networks that are simple and non-hierarchical, whereas OSPF protocol fits best for large and hierarchical enterprise networks. In a complex network, you may have multiple routing protocols operating simultaneously.
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is a distance-vector routing protocol. Routers running the distance-vector protocol send all or a portion of their routing tables in routing-update messages to their neighbors. You can use RIP to configure the hosts as part of a RIP network.
NAT and RIP are different protocols. NAT has the main function of IP address translation, but RIP is a dynamic route protocol. The two protocols are usually used in different aspects of network function.
Questions:
1. What is RIP vs OSPF?
OSPF stands for Open Shortest Path First and is a link-state routing protocol, while RIP stands for Routing Information Protocol and is a distance-vector routing protocol. OSPF uses cost as its metric when deciding which route to take, while RIP uses hop count as its metric.
2. What is the example of RIP?
RIP will automatically summarize routes to the classful boundary by default. For example, if you’ve got an interface with IP address 192.168.10.1/30, and under RIP you include that with a network statement, it will be advertised as 192.168.10.0/24.
3. Why is RIP useful in networks?
The RIP IGP uses the Bellman-Ford, or distance-vector, algorithm to determine the best route to a destination. RIP uses the hop count as the metric. RIP enables hosts and routers to exchange information for computing routes through an IP-based network.
4. What does RIP stand for Cisco?
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is normally a broadcast protocol, and for RIP routing updates to reach nonbroadcast networks, you must configure the Cisco software to permit this exchange of routing information.
5. Why OSPF is better than RIP?
OSPF routing protocol has complete knowledge of network topology, allowing routers to calculate routes based on incoming requests. OSPF protocol has no limitations in hop count, unlike RIP protocol that has only 15 hops at most. So OSPF converges faster than RIP and has better load balancing.
6. Is RIP a BGP?
OSPF and RIP are Interior Gateway Protocols (IGP) and distribute routing information within an autonomous system, whereas BGP is an Exterior Gateway Protocol. The routes learned via the dynamic routing protocols are applied to the kernel routing table.
7. Is RIP used anymore?
It became ubiquitous on headstones in the 18th century and is widely used today when mentioning someone’s death.
8. What is the main disadvantage of using RIP?
This is one of the biggest disadvantages of RIP. Bandwidth utilization in RIP is very high as it broadcasts its updates every 30 seconds. RIP supports only 15 hop count, so a maximum of 16 routers can be configured in RIP. Here the convergence rate is slow.
9. Why is RIP better than OSPF?
After comparing RIP vs OSPF differences, it’s clear that RIP protocol is ideal for small networks that are simple and non-hierarchical, whereas OSPF protocol fits best for large and hierarchical enterprise networks. In a complex network, you may have multiple routing protocols operating simultaneously.
10. How does RIP work as a routing protocol?
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is a distance-vector routing protocol. Routers running the distance-vector protocol send all or a portion of their routing tables in routing-update messages to their neighbors. You can use RIP to configure the hosts as part of a RIP network.
11. What is NAT vs RIP?
NAT and RIP are different protocols. NAT has the main function of IP address translation, but RIP is a dynamic route protocol. The two protocols are usually used in different aspects of network function.
What is RIP vs OSPF
OSPF stands for Open Shortest Path First and is a link-state routing protocol, while RIP stands for Routing Information Protocol and is a distance-vector routing protocol. OSPF uses cost as its metric when deciding which route to take, while RIP uses hop count as its metric.
Cached
What is the example of RIP
RIP will automatically summarize routes to the classful boundary by default. For example, if you've got an interface with IP address 192.168. 10.1/30, and under RIP you include that with a network statement, it will be advertised as 192.168. 10.0/24.
Cached
Why is RIP useful in networks
The RIP IGP uses the Bellman-Ford, or distance-vector, algorithm to determine the best route to a destination. RIP uses the hop count as the metric. RIP enables hosts and routers to exchange information for computing routes through an IP-based network.
Cached
What does RIP stand for Cisco
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is normally a broadcast protocol, and for RIP routing updates to reach nonbroadcast networks, you must configure the Cisco software to permit this exchange of routing information.
Cached
Why OSPF is better than RIP
OSPF routing protocol has complete knowledge of network topology, allowing routers to calculate routes based on incoming requests. OSPF protocol has no limitations in hop count, unlike RIP protocol that has only 15 hops at most. So OSPF converges faster than RIP and has better load balancing.
Is RIP a BGP
OSPF and RIP are Interior Gateway Protocols (IGP) and distribute routing information within an autonomous system, whereas BGP is a Exterior Gateway Protocol. The routes learned via the dynamic routing protocols are applied to the kernel routing table.
Is RIP used anymore
It became ubiquitous on headstones in the 18th century, and is widely used today when mentioning someone's death.
What is the main disadvantage of using RIP
This is one of the biggest disadvantages of RIP. Bandwidth utilization in RIP is very high as it broadcasts its updates every 30 seconds. RIP supports only 15 hop count so a maximum of 16 routers can be configured in RIP. Here the convergence rate is slow.
Why is RIP better than OSPF
Conclusion. After comparing RIP vs OSPF differences, it's clear that RIP protocol is ideal for small networks that are simple and non-hierarchical, whereas OSPF protocol fits best for large and hierarchical enterprise networks. In a complex network, you may have multiple routing protocols operating simultaneously.
How does RIP work as routing protocol
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is a distance-vector routing protocol. Routers running the distance-vector protocol send all or a portion of their routing tables in routing-update messages to their neighbors. You can use RIP to configure the hosts as part of a RIP network.
What is NAT vs RIP
NAT and RIP are different protocol. NAT has main function for ip address translation. But RIP is a dynamic route protocol. The two protocol usually be used in different aspect of network function.
What is RIP vs BGP vs OSPF
OSPF and RIP are Interior Gateway Protocols (IGP) and distribute routing information within an autonomous system, whereas BGP is a Exterior Gateway Protocol. The routes learned via the dynamic routing protocols are applied to the kernel routing table.
Can a router run both OSPF and RIP
The operation of the RIP and OSPF routing protocols is interface dependent. Each interface and virtual sub-interface can have RIP and OSPF settings configured separately, and each interface can run both RIP and OSPF routers.
What is RIP vs OSPF vs BGP
OSPF and RIP are Interior Gateway Protocols (IGP) and distribute routing information within an autonomous system, whereas BGP is a Exterior Gateway Protocol. The routes learned via the dynamic routing protocols are applied to the kernel routing table.
Is RIP a Layer 3 protocol
RIP works at layer 3 and sends routing information across the network.
Is RIP disrespectful
There's nothing wrong with saying “rest in peace” or “rest easy.” In fact, many people find comfort in hearing those phrases after someone dies. However, you don't have to limit yourself to using those sayings if you'd rather say something more unique.
Why is OSPF better than RIP
Pros: OSPF routing protocol has complete knowledge of network topology, allowing routers to calculate routes based on incoming requests. OSPF protocol has no limitations in hop count, unlike RIP protocol that has only 15 hops at most. So OSPF converges faster than RIP and has better load balancing.
Why not use RIP protocol
In most networking environments, RIP is not the preferred choice of routing protocol, as its time to converge and scalability are poor compared to EIGRP, OSPF, or IS-IS. However, it is easy to configure, because RIP does not require any parameters, unlike other protocols.
What are the disadvantages of RIP routing
Disadvantages of RIPBandwidth utilization in RIP is very high as it broadcasts its updates every 30 seconds.RIP supports only 15 hop count so a maximum of 16 routers can be configured in RIP.Here the convergence rate is slow. It means that when any link goes down it takes a lot of time to choose alternate routes.
Is RIP protocol same as BGP
OSPF and RIP are Interior Gateway Protocols (IGP) and distribute routing information within an autonomous system, whereas BGP is a Exterior Gateway Protocol. The routes learned via the dynamic routing protocols are applied to the kernel routing table.
Why use RIP over OSPF
Conclusion. After comparing RIP vs OSPF differences, it's clear that RIP protocol is ideal for small networks that are simple and non-hierarchical, whereas OSPF protocol fits best for large and hierarchical enterprise networks. In a complex network, you may have multiple routing protocols operating simultaneously.
Should I use RIP on my router
RIP is best for small networks. This is because the transmission of the full routing table each 30 seconds can put a large traffic load on the network, and because RIP tables are limited to 15 hops. OSPF is a better alternative for larger networks.
Is RIP a Layer 7 protocol
RIP works at layer 3 and sends routing information across the network.
Is RIP a layer 7
from an IP point of view RIP is an application utilizing transport over IP/UDP. So this justifies to say it is Layer7.
Do people still say RIP
Today, it is more common to find rest in peace or R.I.P. on gravestones and in funeral services than its Latin parent. The acronym R.I.P. appeared first in 1613 as an abbreviation for requiescat in pace, then in 1681 for rest in peace.



