Which is better RIP or OSPF?
Summary:
When comparing the RIP and OSPF routing protocols, it becomes clear that each has its advantages and disadvantages. RIP (Routing Information Protocol) is ideal for small, simple, and non-hierarchical networks, while OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) is better suited for larger, hierarchical enterprise networks. In a complex network, it is possible to have multiple routing protocols operating simultaneously.
1. Which is better RIP or OSPF?
RIP vs OSPF differences highlight that RIP protocol is ideal for small networks that are simple and non-hierarchical, whereas OSPF protocol fits best for large and hierarchical enterprise networks. In a complex network, you may have multiple routing protocols operating simultaneously.
2. Which routing protocol is better RIP or OSPF?
The main difference between RIP and OSPF is that RIP is a Distance Vector protocol that determines the transmission path based on the distance or hops count, while OSPF is a link-state protocol that determines the shortest path by analyzing factors such as speed, cost, and path congestion.
3. Why is OSPF the best?
OSPF is considered the best choice for corporate LANs and private data centers due to its network convergence speed and ability to choose paths based on network performance.
4. Does OSPF have a higher administrative distance than RIP?
The router prefers protocols that have a lower assigned administrative distance. OSPF has a default distance of 110, making it preferred over RIP, which has a default distance of 120.
5. Why not use RIP protocol?
In most networking environments, RIP is not the preferred choice of routing protocol due to its poor time to converge and scalability compared to protocols like EIGRP, OSPF, or IS-IS. However, it is easy to configure as it does not require many parameters.
6. Why is RIP bad for large networks?
RIP uses hop counts only to determine the shortest path to a destination. It limits its paths to a maximum of 15 hops, making it ineffective for large networks. RIP Version 2 supports CIDR and uses IP multicast at address 224.0.
7. Can a router run both OSPF and RIP?
Yes, each interface and virtual sub-interface can have separate RIP and OSPF settings configured, allowing a router to run both protocols.
8. Which routing is more secure?
Static routing is considered more secure as it doesn’t share routes across the entire network. Dynamic routing, such as OSPF, creates more security risks as it shares complete routing tables.
9. What are the disadvantages of OSPF?
Some disadvantages of OSPF include the need for a lot of information to calculate the best route for each destination, the extra CPU processing required to run the SPF algorithm for route calculation, and the complexity of configuration and troubleshooting.
10. Why use RIP protocol?
RIP protocol can be used to configure hosts as part of a RIP network, requiring less maintenance and automatically reconfiguring routing tables when network changes or communication stops.
These are just a few key questions about the RIP and OSPF protocols and their differences. It is important to consider the specific requirements and characteristics of the network before deciding which routing protocol to use.
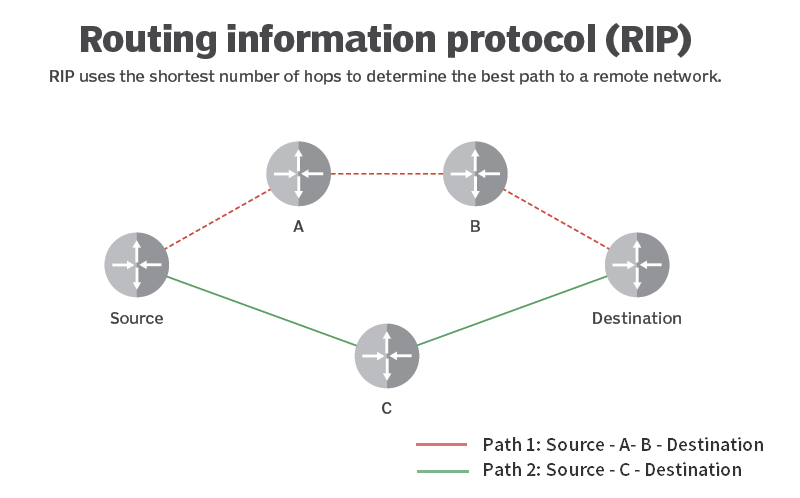
Why is RIP better than OSPF
Conclusion. After comparing RIP vs OSPF differences, it's clear that RIP protocol is ideal for small networks that are simple and non-hierarchical, whereas OSPF protocol fits best for large and hierarchical enterprise networks. In a complex network, you may have multiple routing protocols operating simultaneously.
Which routing protocol is better RIP or OSPF
Difference between RIP and OSPF
| RIP | OSPF |
|---|---|
| It's a Distance Vector protocol that determines the transmission path based on the distance or hops count. | It is a link-state protocol that determines the shortest path by analyzing many factors such as speed, cost, and path congestion. |
Cached
Why is OSPF the best
Network convergence is the speed at which a router can adjust the path used to a destination network if a network outage occurs. Because of its convergence speed and ability to choose paths based on network performance, OSPF is a better choice within corporate LANs and private data centers.
Does OSPF have a higher ad than RIP
The router prefers protocols that have a lower assigned administrative distance. For example, OSPF has a default distance of 110, so it is preferred by the router process, over RIP, which has a default distance of 120.
Why not use RIP protocol
In most networking environments, RIP is not the preferred choice of routing protocol, as its time to converge and scalability are poor compared to EIGRP, OSPF, or IS-IS. However, it is easy to configure, because RIP does not require any parameters, unlike other protocols.
Why is RIP bad for large networks
RIP uses hop counts only to determine the shortest path to a destination. To avoid loops, RIP limits its paths to a maximum of 15 hops, making it an ineffective protocol for large networks. RIP Version 2 supports Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) and uses IP multicast at address 224.0.
Can a router run both OSPF and RIP
The operation of the RIP and OSPF routing protocols is interface dependent. Each interface and virtual sub-interface can have RIP and OSPF settings configured separately, and each interface can run both RIP and OSPF routers.
Which routing is more secure
Static routing
Static routing is more secure because it doesn't share routes across the entire network. Dynamic routing creates more security risks because it shares complete routing tables across the network.
What is OSPF disadvantages
Disadvantages OSPFIt needs lots of information to calculate the best route for each destination.To calculate the best route, it runs the SPF algorithm that requires extra CPU processing.It is complex to configure and difficult to troubleshoot.
Why use RIP protocol
You can use RIP to configure the hosts as part of a RIP network. This type of routing requires little maintenance and also automatically reconfigures routing tables when your network changes or network communication stops.
What is the main disadvantage of using RIP
This is one of the biggest disadvantages of RIP. Bandwidth utilization in RIP is very high as it broadcasts its updates every 30 seconds. RIP supports only 15 hop count so a maximum of 16 routers can be configured in RIP. Here the convergence rate is slow.
What is the main disadvantage of using a RIP
The disadvantages of RIP include:
Increased network traffic: RIP checks with its neighboring routers every 30 seconds, which increases network traffic. Maximum hop count: RIP has a maximum hop count of 15, which means that on large networks, other remote routers may not be able to be reached.
What is RIP protocol weakness
Disadvantages of RIPBandwidth utilization in RIP is very high as it broadcasts its updates every 30 seconds.RIP supports only 15 hop count so a maximum of 16 routers can be configured in RIP.Here the convergence rate is slow. It means that when any link goes down it takes a lot of time to choose alternate routes.
Is RIP outdated
It is the oldest routing protocol used by the network industry and is considered by many to be inefficient or border-line obsolete. However for CCNA students it important to understand RIP, as well as how to configure and troubleshoot it.
What is the main disadvantages of using RIP
The disadvantages of RIP include:
Increased network traffic: RIP checks with its neighboring routers every 30 seconds, which increases network traffic. Maximum hop count: RIP has a maximum hop count of 15, which means that on large networks, other remote routers may not be able to be reached.
What are the disadvantages of OSPF
Disadvantages OSPFIt needs lots of information to calculate the best route for each destination.To calculate the best route, it runs the SPF algorithm that requires extra CPU processing.It is complex to configure and difficult to troubleshoot.
What are some common problems with RIP
Problems With RIP's Basic Algorithm and Implementation
The are four main problems here: slow convergence, routing loops, “counting to infinity” and “small infinity”.
Which type of routing is preferred
Metric – In the event there are multiple routes learned by the same protocol with same prefix length, the route with the lowest metric is preferred. (If two or more of these routes have equal metrics, load balancing across them may occur.)
Which is a perfect routing protocol
Some of the most common routing protocols include RIP, IGRP, EIGRP, OSPF, IS-IS and BGP. There are two primary routing protocol types although many different routing protocols defined with those two types. Link state and distance vector protocols comprise the primary types.
What is the advantage of RIP
Advantages of RIP
easy to understand. predominantly loop-free. guaranteed to support almost all routers. promotes load balancing.
What is better than OSPF
While OSPF uses cost as a metric to determine the best path, BGP uses BGP attributes to determine the best path. Because it is not uncommon to have multiple paths to the same destination, BGP has a best-path selection algorithm to eventually choose the best path (or paths, if BGP multipath is configured).
What are the disadvantages of RIP protocol
Disadvantages of RIPBandwidth utilization in RIP is very high as it broadcasts its updates every 30 seconds.RIP supports only 15 hop count so a maximum of 16 routers can be configured in RIP.Here the convergence rate is slow. It means that when any link goes down it takes a lot of time to choose alternate routes.
What is the problem with RIP
The are four main problems here: slow convergence, routing loops, “counting to infinity” and “small infinity”. The distance-vector algorithm is designed so that all routers share all their routing information regularly.
Why is RIP not used in large networks
RIP has been supplanted mainly due to its simplicity and inability to scale to very large and complex networks. Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is another distance vector protocol that is now used to transfer routing information across autonomous systems on the internet.
What are the weaknesses of RIP protocol
Limitations of RIPInability to support paths longer than 15 hops.Reliance on fixed metrics to calculate routes.Network intensity of table updates.Relatively slow convergence.Lack of support for dynamic load balancing.



