Why do we encrypt data?
Summary of the Article: Why do we encrypt data?
Encryption is used to protect data from being stolen, changed, or compromised. It works by scrambling data into a secret code that can only be unlocked with a unique digital key. The main reason to encrypt a file is to protect its contents from being read by anyone who doesn’t have the encryption key. Encryption serves three purposes – keeping data confidential, authenticating its origin, ensuring data integrity, and preventing senders from denying they sent an encrypted message (non-repudiation). All organizations that collect personally identifiable information (PII) must secure that data through encryption.
There are several benefits of encrypting files. Encryption technology is cheap to implement and can save you from regulatory fines. It also helps to protect remote workers and increase the integrity of data, boosting consumer trust. Files that contain personally identifiable information or sensitive information should be encrypted to ensure their security. Cryptography has four major goals – confidentiality, integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation. The most commonly used encryption method is the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), which is employed by many government bodies worldwide. The three primary encryption types are DES, AES, and RSA, with 3DES providing triple protection using three independent 56-bit keys. While not all data needs to be encrypted, it is generally recommended to err on the side of caution and use encryption to protect both the data and oneself.
Questions:
1. What is the purpose of encryption?
The purpose of encryption is to protect data from being stolen, changed, or compromised. It works by scrambling data into a secret code that can only be unlocked with a unique digital key.
2. What is the main reason to encrypt a file?
The main reason to encrypt a file is to protect its contents from being read by anyone who doesn’t have the encryption key.
3. What are three purposes of encryption?
Encryption serves three purposes – keeping data confidential, authenticating its origin, ensuring data integrity, and preventing senders from denying they sent an encrypted message (non-repudiation).
4. What data should be encrypted?
All organizations that collect personally identifiable information (PII) like names, birthdates, Social Security numbers, and financial information must secure that data.
5. What are the benefits of encrypting a file?
Encrypting files has several benefits. It is cost-effective to implement, saves you from regulatory fines, helps protect remote workers, increases data integrity, and boosts consumer trust.
6. When should you encrypt files?
As a general rule of thumb, encrypt any files that have personally identifiable information or contain information or images you wouldn’t want published online for anyone to see.
7. What are the four objectives of encryption?
The four objectives of encryption are confidentiality, integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation.
8. What is the most common use for encryption?
The most commonly used encryption method is the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), which is employed by many government bodies worldwide.
9. What are the three types of data that can be encrypted?
The three primary encryption types are DES, AES, and RSA. 3DES, which utilizes three independent 56-bit keys, is still in use today.
10. Does all data need to be encrypted?
While not all data needs to be encrypted, it is generally recommended to use encryption to protect both the data and oneself.
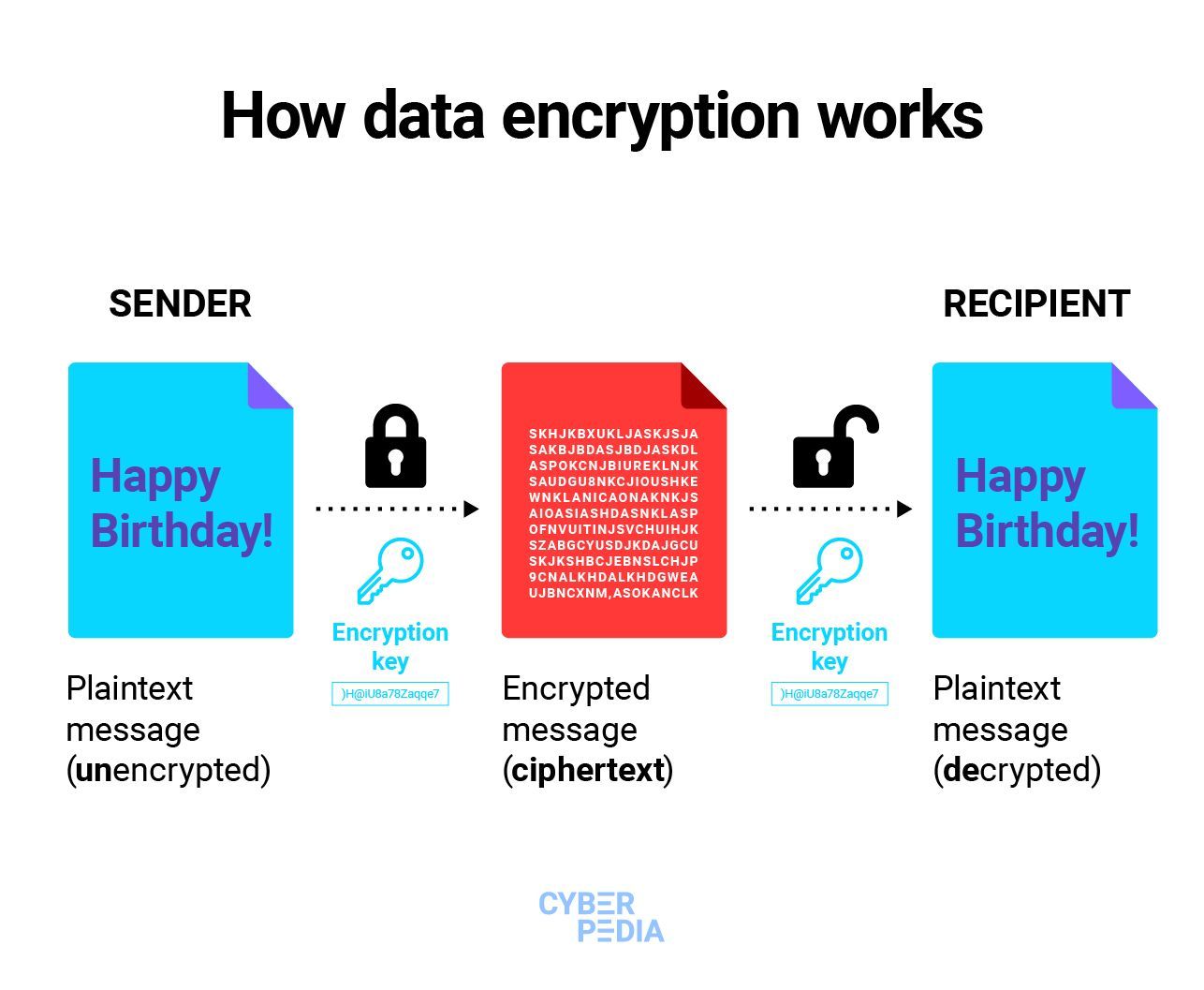
What is the purpose of encrypted
Encryption is used to protect data from being stolen, changed, or compromised and works by scrambling data into a secret code that can only be unlocked with a unique digital key.
What is the main reason to encrypt a file
Encryption protects the contents of a file from being read by anyone who doesn't have the encryption key.
What are 3 purposes of encryption
Not only does it keep the data confidential, but it can authenticate its origin, ensure that data has not changed after it was sent, and prevent senders from denying they sent an encrypted message (also known as nonrepudiation).
What data should be encrypted
The purpose of file and disk encryption is to protect data stored on a computer or network storage system. All organizations that collect personally identifiable information (PII) like names, birthdates, Social Security numbers and financial information must secure that data.
What are the benefits of encrypting a file
Benefits of Using Encryption Technology for Data SecurityEncryption is Cheap to Implement.Encryption Can Save You from Regulatory Fines.Encryption Can Help to Protect Remote Workers.Encryption Increases the Integrity of Our Data.Encryption Can Increase Consumer Trust.
When should you encrypt files
As a general rule of thumb, encrypt any files that have personally identifiable information, or have information or images you wouldn't want published online for anyone to see.
What are the 4 objectives of encryption
Cryptography has four major goals: confidentiality, integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation.
What is the most common use for encryption
1. Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) The Advanced Encryption Standard is a symmetric encryption algorithm that is the most frequently used method of data encryption globally. Often referred to as the gold standard for data encryption, AES is used by many government bodies worldwide, including in the U.S.
What are the 3 types of data that can be encrypted
DES, AES, and RSA are the three primary encryption types. A more recent 3DES is a block cipher that is still in use today. The Triple Data Encryption Standard (3DES) does exactly what its name says. For triple protection, it employs three independent 56-bit keys rather than a single 56-bit key.
Does all data need to be encrypted
Final Thoughts. It is ultimately up to you, the user, on whether or not you feel your data should be encrypted. In most cases it is best to err on the side of caution and use encryption to not only protect the data but protect yourself and the university.
What are two advantages of encrypting data
Benefits of Using Encryption Technology for Data SecurityEncryption is Cheap to Implement.Encryption Can Save You from Regulatory Fines.Encryption Can Help to Protect Remote Workers.Encryption Increases the Integrity of Our Data.Encryption Can Increase Consumer Trust.
What files usually need to be encrypted
Below are some of the most common use cases and file types that require encryption.Banking documents. One obvious use case for file encryption is banking documents.Work files.Hard drive backups.Images.Videos.Documents.PDFs.Spreadsheets.
What files must be encrypted
Here are three key types that you should definitely encrypt.HR data. Unless you're a sole trader, every company has employees, and this comes with a large amount of sensitive data that must be protected.Commercial information.Legal information.
What are the three goals of encryption
Goals of CryptographyData Privacy(confidentiality)Data Authenticity(it came from from where it claims)Data integrity(it has not been modified on the way) in the digital world.
What are three 3 methods for encrypting data
3 Types of Encryption to Protect Your DataSymmetric. The symmetric encryption method uses a single key both to encrypt and decrypt the data.Asymmetric. The second major encryption method is asymmetric encryption, also sometimes known as public key encryption.Hashing.
What is data encryption and when it is needed
Data encryption converts data from a readable, plaintext format into an unreadable, encoded format: ciphertext. Users and processes can only read and process encrypted data after it is decrypted. The decryption key is secret, so it must be protected against unauthorized access.
What are the 2 main types of encryption
There are two types of encryption in widespread use today: symmetric and asymmetric encryption. The name derives from whether or not the same key is used for encryption and decryption.
What type of data must be encrypted
In broad terms, there are two types of data you should encrypt: personally identifiable information and confidential business intellectual property. Personally Identifiable Information (PII)PII includes any kind of information another person can use to uniquely identify you.
What happens if data is not encrypted
If the data is not encrypted and only HTTPS is in place, the data is in readable form before being sent further inside the private network protected by a firewall. Operators of the firewall can intercept, change or manipulate the data.
What happens if you don’t encrypt data
Unprotected Data in Use Makes You Vulnerable
A great deal of data is available for hackers to access and exploit. An attacker targeting a specific company's databases could go to LinkedIn and quickly find a few employees who are likely to have admin access to enterprise IT resources.
How does encryption protect files
File encryption or file-based encryption is the process of protecting individual files on a system using encryption algorithms. It scrambles data into an unintelligible form that a user can decode or decrypt with the help of cryptographic keys.
What does encrypt contents to secure data do
Encrypting content to secure data is a process of encoding information so that it can only be accessed by those with the correct authorization. It is a way of protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access, and is used by organizations to protect their data from cyber-attacks.
What are the two basic principles of encryption
With the use of conventional algorithm, the principal security problem is maintaining the secrecy of the key. All the encryption algorithms make use of two general principles; substitution and transposition through which plaintext elements are rearranged. Important thing is that no information should be lost.
Is it better to always encrypt data
Avoid Security Attacks
Security attacks are inevitable, but with better security and data encryption methods, intruders might not analyse or decrypt to understand the data further in a data breach. Suppose a Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack or eavesdropping is happening during backup or transfers between servers.
What are the three 3 different encryption methods
DES, AES, and RSA are the three primary encryption types. A more recent 3DES is a block cipher that is still in use today. The Triple Data Encryption Standard (3DES) does exactly what its name says. For triple protection, it employs three independent 56-bit keys rather than a single 56-bit key.



