Why is SSO important?
Summary of the article:
SSO solutions enable IT teams to track and monitor the applications that users access. Moreover, SSO solutions also provide IT the ability to control what resources users can access. All these capabilities are provided through a single solution, thereby streamlining application access control initiatives.
Not only does SSO eliminate tasks, but it also helps with such functions as user-activity management and user-account oversight. However, it also carries a major security risk. A hacker who is able to gain control of a user’s credentials may be able to penetrate every application to which the user has access.
SSO is strictly related to the authentication part of a federated identity system. Its only concern is establishing the identity of the user and then sharing that information with each subsystem that requires the data.
The user experience of single sign-on (SSO), two-factor authentication (2FA), and multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a much smoother and more secure experience for users. SSO allows users to log in to multiple sites and applications with just one set of credentials.
From large-scale inefficiency to help desk overflow, not having SSO in place makes organizations and users more vulnerable than ever. The most noticeable difference when SSO is removed is the sudden and immediate need for multiple passwords.
Key benefits of seamless SSO include a great user experience and the ease of deployment and administration. Users are automatically signed into both on-premises and cloud-based applications without having to enter passwords repeatedly.
Since SSO is linked to many critical resources, if an SSO provider is targeted by an attack, entire user bases will be compromised. If an end user’s SSO portal is compromised, then their access to those applications is also at risk if MFA isn’t being utilized.
Having an SSO solution in place enables applications to be protected with either passwordless authentication or unique, high-entropy passwords, making them more secure than when an employee is charged with creating and managing password access to these applications.
For security reasons, the SSO login flow must complete within a certain timeframe, or authentication fails. If the clock on your Identity Provider is incorrect, most or all login attempts will appear to be out of the acceptable timeframe, and authentication will fail.
The most noticeable difference when SSO is removed is the sudden and immediate need for multiple passwords. While SSO enables users to log in with a single, secure password, non-SSO means that a user is required to log into each individual account that they are using each time they want to access it.
The difference between authentication and SSO is that authentication verifies the identity of a user, while SSO is a method that allows users to authenticate themselves once and gain access to multiple systems without having to log in again.
Questions:
- What is the benefits of SSO?
- What are the pros and cons of SSO?
- What is the main concern with single sign-on?
- Is SSO strong authentication?
- What are the risks of not implementing SSO?
- What are the two key benefits of seamless SSO?
- What was one of the most important potential drawbacks of SSO?
- Does single sign-on improve security?
- What happens when SSO fails?
- What is the risk of not using SSO?
- What is the difference between authentication and SSO?
Answer: SSO solutions streamline application access control and provide IT teams with the ability to track and monitor user access to applications. It also enables IT to control user access to resources through a single solution.
Answer: Some pros of SSO include eliminating tasks, user-activity management, and user-account oversight. However, a major con is the security risk it poses if a hacker gains control of user credentials.
Answer: The main concern with single sign-on is establishing a user’s identity and sharing that information with subsystems that require it in a federated identity system.
Answer: SSO, along with two-factor authentication (2FA) and multi-factor authentication (MFA), provides a smoother and more secure user experience. SSO allows users to log in to multiple sites and applications using a single set of credentials.
Answer: Not implementing SSO can lead to inefficiency, help desk overflow, and increased vulnerability. The most noticeable difference is the need for multiple passwords without SSO.
Answer: The key benefits of seamless SSO are a great user experience and easy deployment and administration. Users are automatically signed into on-premises and cloud-based applications without repeatedly entering passwords.
Answer: One potential drawback of SSO is that if an SSO provider is targeted by an attack, it can compromise the entire user base. If an end user’s SSO portal is compromised and MFA isn’t utilized, their access to applications is also at risk.
Answer: Having an SSO solution in place can improve security by protecting applications through passwordless authentication or unique, high-entropy passwords.
Answer: When SSO fails, the SSO login flow must complete within a certain timeframe for security reasons. If the clock on the Identity Provider is incorrect, authentication will fail.
Answer: Not using SSO means users need to log into each individual account with separate credentials, leading to the need for multiple passwords and increased access management challenges.
Answer: Authentication verifies a user’s identity, while SSO allows users to authenticate themselves once and gain access to multiple systems without logging in again.
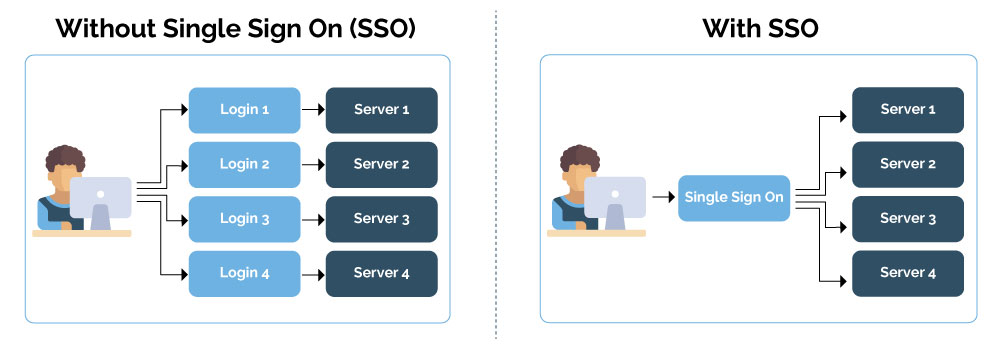
What is the benefits of SSO
SSO solutions enable IT teams to track and monitor the applications that users access. Moreover, SSO solutions also provide IT the ability to control what resources users can access. All these capabilities are provided through a single solution, thereby streamlining application access control initiatives.
Cached
What are the pros and cons of SSO
Not only does SSO eliminate tasks, but it also helps with such functions as user-activity management and user-account oversight. However, it also carries a major security risk. A hacker who is able to gain control of a user's credentials may be able to penetrate every application to which the user has access.
Cached
What is the main concern with single sign-on
SSO is strictly related to the authentication part of a federated identity system. Its only concern is establishing the identity of the user and then sharing that information with each subsystem that requires the data.
CachedSimilar
Is SSO strong authentication
The user experience of single sign-on (SSO), two-factor authentication (2FA) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a much smoother and more secure experience for users. SSO allows users to log in to multiple sites and applications with just one set of credentials.
What are the risks of not implementing SSO
From large-scale inefficiency to help desk overflow, not having SSO in place makes organizations and users more vulnerable than ever. The most noticeable difference when SSO is removed is the sudden and immediate need for multiple passwords.
What are the two key benefits of seamless SSO
Key benefitsGreat user experience. Users are automatically signed into both on-premises and cloud-based applications. Users don't have to enter their passwords repeatedly.Easy to deploy & administer. No additional components needed on-premises to make this work.
What was one of the most important potential drawbacks of SSO
Since SSO is linked to many critical resources, if an SSO provider is targeted by an attack, entire user bases will be compromised. If an end user's SSO portal is compromised, then their access to those applications is also at risk if MFA isn't being utilized.
Does single sign-on improve security
Having an SSO solution in place enables these apps to be protected, either by passwordless authentication, or unique, high-entropy passwords, making them orders of magnitude more secure than when an employee is charged with creating and managing password access to these applications.
What happens when SSO fails
For security reasons, the SSO login flow must complete within a certain timeframe, or authentication fails. If the clock on your Identity Provider is incorrect, most or all login attempts will appear to be out of the acceptable timeframe, and authentication will fail with the above error message.
What is the risk of not using SSO
The most noticeable difference when SSO is removed is the sudden and immediate need for multiple passwords. While SSO enables users to log in with a single, secure password, non-SSO means that a user is required to log into each individual account that they are using each time they want to access it.
What is the difference between authentication and SSO
The main difference between MFA and SSO is that MFA is a type of authentication that alleviates the low security of passwords by introducing an extra layer of security, whereas SSO is a cloud security technology that mitigates the hassle of reentering the password by asking the user to type their password only once per …
Is SSO better for security
Improved Security
With SSO, users only need to remember a single password for all their applications and are more likely to secure passphrases. They are also less likely to reuse passwords or write them down, which reduces the risk of theft.
Is SSO more or less secure
SSO is one of the most secure ways to authenticate a user. However, as usual, it depends on how the deployment is made. The access to the SSO platform (Microsoft, OneLogin, Okta, …) should be protected with a strong 2FA/MFA method, passwordless if possible.
What is SSO and what are some of the key examples of IT in use
The user signs in only one time, hence the name of the feature (Single Sign-on). For example, if you log in to a Google service such as Gmail, you are automatically authenticated to YouTube, AdSense, Google Analytics, and other Google apps.
What is the difference between SSO and seamless SSO
Single sign on (SSO) is an authentication method that lets you use a single username and password to access multiple applications. Seamless SSO occurs when a user is automatically signed into their connected applications when they're on corporate desktops connected to the corporate network.
Is SSO a security risk
SSO, like any other form of access, brings implied security vulnerabilities. While those risks can be minimized by implementing additional controls, like multi-factor authentication (MFA) and session management, identifying the dangers of single sign-on helps ensure that your organization implements a secure solution.
How does SSO prevent phishing
Rather than making users feel guilty for being gullible, single sign-on (SSO) solutions like Duo SSO complement MFA to mitigate phishing risks by enabling users to use a single set of credentials to access multiple applications.
Is SSO a security control
However, an important question to consider is: “is SSO secure” Although the main features of SSO include improved IT monitoring and management, and security control, the technology itself is primarily designed to improve productivity, often at the cost of security.
Does SSO improve security
Improved Security
With SSO, users only need to remember a single password for all their applications and are more likely to secure passphrases. They are also less likely to reuse passwords or write them down, which reduces the risk of theft.
What do you need to implement SSO
Most SaaS applications have their own user directories. For SSO implementation to happen, you will need to get these different user directories on the same page. This can be done through various third-party vendors that have developed a single point of integration to use across all of your different platforms.
How does SSO help keep the cloud secure
Security and compliance benefits of SSO
SSO reduces the number of attack surfaces because users only log in once each day and only use one set of credentials. Reducing login to one set of credentials improves enterprise security.
Why is SSO so secure
Security and compliance benefits of SSO
SSO reduces the number of attack surfaces because users only log in once each day and only use one set of credentials. Reducing login to one set of credentials improves enterprise security. When employees have to use separate passwords for each app, they usually don't.
What are 3 ways to prevent phishing attacks
Tips to Prevent Phishing AttacksKnow what a phishing scam looks like.Don't click on that link.Get free anti-phishing add-ons.Don't give your information to an unsecured site.Rotate passwords regularly.Don't ignore those updates.Install firewalls.Don't be tempted by those pop-ups.
What is the strategy of SSO
Single-Sign On (SSO) describes an identity solution that allows multiple applications to use the same authentication session, so avoiding repetitive credential entry. SSO implementations are often adopted by companies in the enterprise world as part of their strategy to secure access to important resources.
What is SSO and how do you implement IT
Single Sign On Authentication provides your users with a seamless authentication experience when they navigate either through the applications you have built and/or third party apps. Once your users log in to one of these applications, they won't have to enter their credentials again when accessing another one.



