Does carbon monoxide rise or drop?
Does carbon monoxide go low?
When placing your CO detectors, keep in mind where carbon monoxide gas tends to settle in the air. Because CO is slightly less dense than air, it rises. It then can cause CO poisoning because it stays in the air over an extended period.
Can carbon monoxide rise to the second floor?
Dangerous carbon monoxide buildup is often trapped on a single floor of your home. The main living and sleeping areas upstairs may be just fine, but if the furnace or water heater in the basement starts malfunctioning, a release of CO gas here could make going downstairs a deadly trap.
Does carbon monoxide rise from the ground?
CO gas is lighter than air, meaning it can rise. It also tends to be found in warm spaces, which further encourages it to rise, so carbon monoxide detectors should always be placed up to five feet off the ground. If you’re unsure, simply attach it to the ceiling as you would a smoke detector.
Where does carbon monoxide sit in a house?
The International Association of Fire Chiefs recommends a carbon monoxide detector on every floor of your home, including the basement. A detector should be located within 10 feet of each bedroom door and there should be one near or over any attached garage.
Does carbon monoxide stay high or low in a room?
There’s a myth that carbon monoxide alarms should be installed lower on the wall because carbon monoxide is heavier than air. In fact, carbon monoxide is slightly lighter than air and diffuses evenly throughout the room.
Does CO2 rise or fall in a room?
Typically, carbon dioxide levels rise during the night when people are sleeping, especially if the door and windows are closed. The concentrations then fall during the day if the room is unoccupied. Unfortunately, poor air quality can hinder restful sleep and optimum health in many homes.
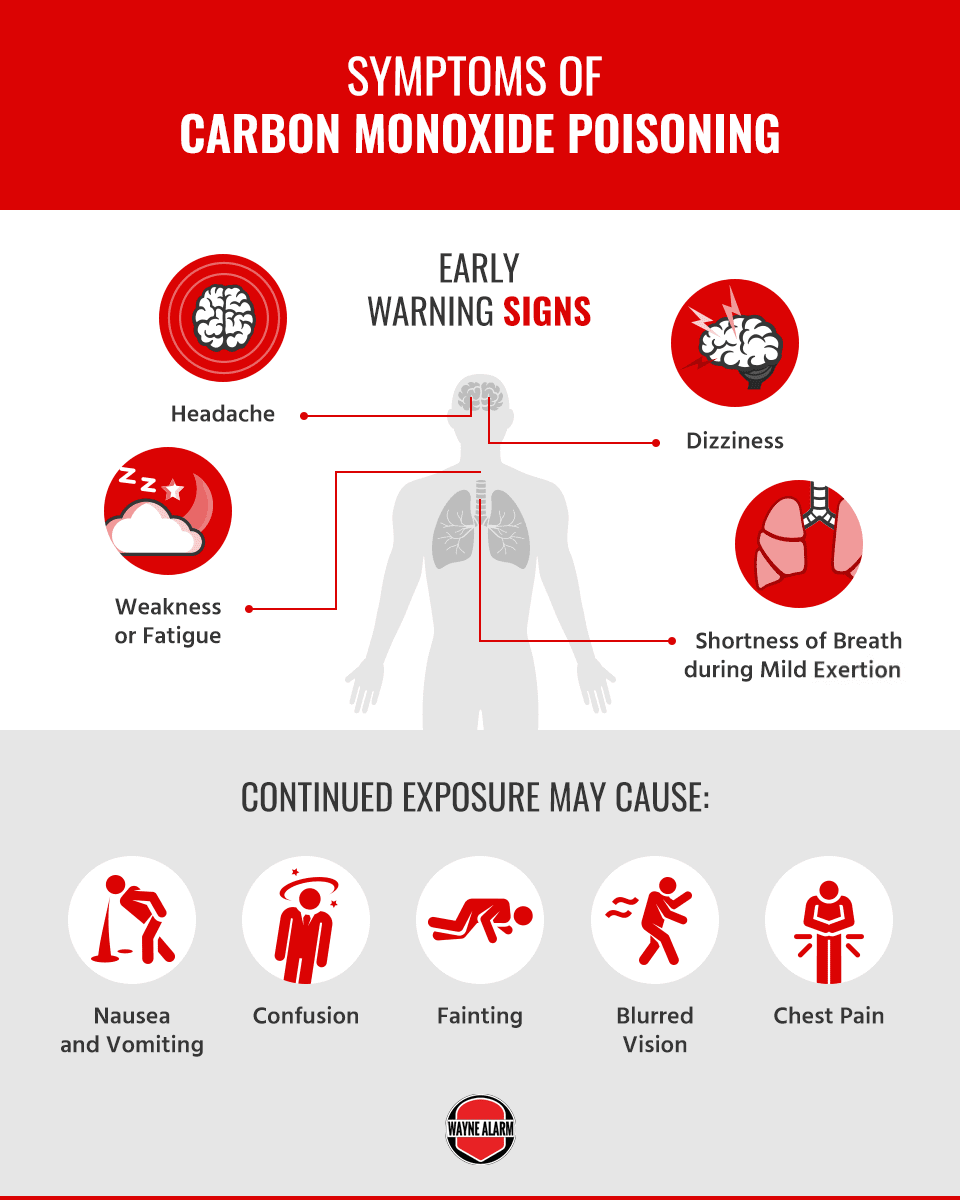
What are two warning signs of carbon monoxide poisoning?
The most common symptoms of CO poisoning are headache, dizziness, weakness, upset stomach, vomiting, chest pain, and confusion. CO symptoms are often described as “flu-like.” If you breathe in a lot of CO it can make you pass out or kill you.
Can carbon monoxide go through walls?
There are experiments in literature that use various VOC that prove gases are able to migrate through the pores in the walls. As CO is a smaller molecule than these, it can be concluded that it can diffuse at least as fast as those.
Does carbon monoxide go to the floor or ceiling?
The specific gravity of Carbon Monoxide is 0.9657 (with normal air being 1.0), this means that it will float up towards the ceiling because it is lighter than regular air.
Does CO2 rise or fall in a room?
Typically, carbon dioxide levels rise during the night when people are sleeping, especially if the door and windows are closed. The concentrations then fall during the day if the room is unoccupied. Unfortunately, poor air quality can hinder restful sleep and optimum health in many homes.
How fast does carbon monoxide leave a room?
Carbon Monoxide Levels:
| Parts Per Million | Response Time |
|---|---|
| 50 ppm | 8 hours |
| 70 ppm | 1 to 4 hours |
| Parts Per Million | Response Time |
|---|---|
| 50 ppm | 8 hours |
| 70 ppm | 1 to 4 hours |
| 150 ppm | 10 to 50 minutes |
| 400 ppm | 4 to 15 minutes |
Does carbon monoxide go on wall or ceiling
Carbon monoxide (CO) and combination alarms should be mounted in or near bedrooms and living areas, on a wall place six inches below the ceiling to six inches above the floor. If mounting on a ceiling, make sure it is at least six inches away from the wall.
Does carbon dioxide go to floor or ceiling
CO2 is heavier than CO. For this reason, a CO2 detector should be near the floor while a CO detector should be placed near the ceiling to ensure proper detection.
How fast does carbon monoxide cause symptoms
Carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning can become deadly in a matter of minutes. If you suspect CO poisoning, leave your home or building immediately and call 911 or go to the emergency room. If treated quickly, the effects of CO poisoning can be reversed.
How can you tell if there is carbon monoxide in your house
A carbon monoxide detector is a must for any home and just as important as a smoke detector. CO detectors should be placed near all bedrooms; they're the only way you will know if carbon monoxide is affecting the air quality in your home, and can help prevent serious illness and even death.
Should carbon monoxide detector be placed high or low
Carbon monoxide is lighter than air. It also rises with warm air, so the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recommends placing a carbon monoxide detector on a wall about five feet above the floor or about eye level. You can put them on the ceiling, too.
How do you know if there is carbon monoxide in the room
A carbon monoxide detector is a must for any home and just as important as a smoke detector. CO detectors should be placed near all bedrooms; they're the only way you will know if carbon monoxide is affecting the air quality in your home, and can help prevent serious illness and even death.
Does opening windows get rid of carbon monoxide
Opening windows does not provide enough ventilation to be protective. CO is an invisible, odorless gas that can be fatal. If you breathe in a lot of CO gas, it can make you pass out or kill you.
Does carbon monoxide stay in drywall
The gypsum material found in drywall contains microscopic pores. The average size of each pore is up to one million times larger than carbon monoxide molecules. Under the right conditions, CO gas from outdoor sources may flow through these pores and infiltrate your home's interior space.
Is there any way to tell if carbon monoxide is in the air
Carbon monoxide gas is colourless and does not smell, so you cannot tell if it is around you.
Does carbon monoxide go through walls
There's a myth that carbon monoxide alarms should be installed lower on the wall because carbon monoxide is heavier than air. In fact, carbon monoxide is slightly lighter than air and diffuses evenly throughout the room.
Will carbon monoxide always rise to the ceiling
The specific gravity of Carbon Monoxide is 0.9657 (with normal air being 1.0), this means that it will float up towards the ceiling because it is lighter than regular air.
What does slow carbon monoxide poisoning feel like
A tension-type headache is the most common symptom of mild carbon monoxide poisoning. Other symptoms include: dizziness. nausea (feeling sick) and vomiting.
What are the six signs of carbon monoxide poisoning
The most common symptoms of CO poisoning are headache, dizziness, weakness, nausea, vomiting, chest pain, and confusion.
How can I check my carbon monoxide levels without a detector
Here are some ways to identify potential carbon monoxide leaks:Brownish or yellowish stains around appliances.A pilot light that frequently goes out.Burner flame appears yellow instead of clear blue (exception: natural gas fireplaces)No upward draft in chimney flue.Stale-smelling air.